7,504,979
System and Method for Providing an Ultra Low Power Scalable DAC Architecture
Patent Number
Issue Date
Inventor(s)
Robert Bowman; Imre Knausz
Document
Download PDF for patent 7,504,979Synopsis
Patent US 7,504,979 B1 describes a system and method for providing an ultra-low power scalable digital-to-analog converter (DAC) architecture, addressing the critical need for power-efficient and highly scalable DACs in modern electronic systems. Traditional DAC designs often face challenges in simultaneously achieving low power consumption, high resolution, and compact size, particularly as the demand for more complex and integrated circuits grows. This invention introduces a novel approach to overcome these limitations.
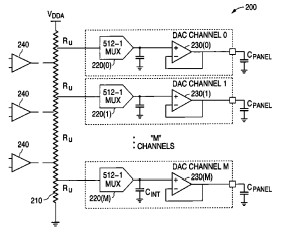
A core innovation of this patent is the utilization of a buffered resistor (R)-string architecture, which forms the basis for a highly efficient DAC. The invention's key features include:
-
Segmented R-string with Buffered Outputs: The DAC employs a resistor string divided into multiple segments, with buffers strategically placed between these segments and at the final outputs. These buffers minimize the current drawn from the resistor string, significantly reducing static power consumption.
-
Low Power Scaling: The architecture is designed to maintain ultra-low power consumption even as the number of output channels increases. This scalability is achieved by the segmented and buffered design, which ensures that power consumption scales linearly or near-linearly with increased resolution or channel count, unlike conventional designs where power can increase exponentially.
-
Compact Layout: The physical layout of the DAC is optimized to be compact, making it suitable for integration into system-on-chip (SoC) designs where real estate is a premium.
-
Reduced Settling Time: The buffered design helps in reducing the settling time of the DAC outputs, which is crucial for high-speed applications.
-
Robustness: The architecture inherently offers improved robustness against variations in process, voltage, and temperature (PVT), making it reliable across a wide range of operating conditions.
The commercial potential for this ultra-low power scalable DAC technology is substantial, particularly in power-sensitive applications where long battery life, compact size, and high performance are paramount. The ability to integrate high-resolution DACs with minimal power overhead opens significant opportunities across various industries.
Possible applications include:
-
Portable and Battery-Powered Devices: Revolutionizing smartphones, tablets, wearables, and other portable electronic devices by enabling longer battery life due to significantly reduced power consumption in the audio, display, and communication subsystems.
-
Internet of Things (IoT) Sensors and Edge Devices: Providing efficient analog signal generation for a vast network of IoT sensors and low-power edge computing devices, allowing for extended deployment times without frequent battery replacement or recharging.
-
Medical Implants and Wearable Health Monitors: Facilitating compact, low-power, and high-precision signal generation for devices like pacemakers, hearing aids, continuous glucose monitors, and other implantable or wearable health technologies, improving patient comfort and device longevity.
-
Automotive Electronics: Enhancing the performance and power efficiency of infotainment systems, sensor interfaces, and control systems in modern vehicles.
-
Industrial Control Systems: Enabling high-accuracy and stable analog outputs for industrial automation and control, particularly in remote or power-constrained environments.
This advanced DAC technology offers a compelling solution for the pervasive demand for power-efficient and scalable analog-to-digital conversion, presenting a valuable licensing opportunity for companies at the forefront of semiconductor manufacturing, consumer electronics, and specialized industrial and medical device development.