8,580,087
Self-Regenerating Particulate Trap Systems for Emissions and Methods Thereof
Patent Number
Issue Date
Inventor(s)
Ali Ogut; Cheng Chen
Document
Download PDF for patent 8,580,087Synopsis
Patent 8,580,087 B2 describes a groundbreaking self-regenerating particulate trap system and method for treating emissions, addressing critical shortcomings of existing emission control technologies. This invention offers a robust, efficient, and low-maintenance solution for eliminating particulate matter from exhaust streams.
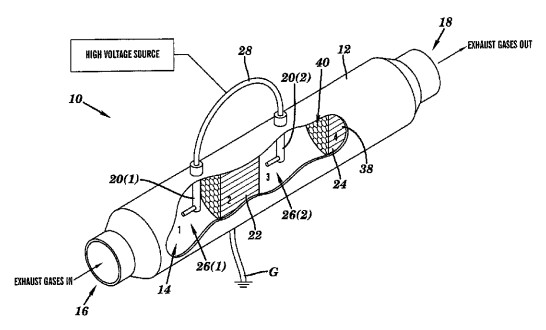
A key novel aspect of this invention lies in its multi-stage emission treatment process. It begins by charging particles in an exhaust stream, then produces reactive radicals. A portion of these radicals are used to oxidize the charged particles. Subsequently, charged particles are attracted to a self-regenerating attraction surface, which is either oppositely charged or grounded. The attracted particles are then oxidized by another portion of the produced radicals, effectively cleaning the attraction surface and allowing continuous operation without manual intervention or energy-intensive thermal regeneration. Furthermore, downstream processes convert other harmful compounds in the exhaust into less hazardous forms, with any remaining charged particles oxidized into gases.
This system stands apart from conventional filtration devices, which are prone to clogging, increase exhaust backpressure, and demand significant energy for regeneration. By leveraging non-thermal plasma for particle separation and trapping, the invention achieves high power efficiency. The self-oxidation of carbon particulates ensures the continuous regeneration of the catalyzed electrostatic surface, significantly reducing the need for maintenance and improving durability. Additionally, the system boasts a lower weight and reduced system pressure drop compared to prior art units, contributing to overall operational efficiency.
The commercial potential for this technology is substantial, particularly in industries grappling with stringent emission regulations and seeking sustainable, cost-effective environmental solutions. Possible applications include:
-
Automotive Industry: Integration into diesel and gasoline vehicles for advanced particulate matter control, enhancing compliance with emissions standards and improving air quality in urban environments. The system's low maintenance and self-regeneration capabilities are highly desirable for vehicle manufacturers and owners.
-
Power Generation: Implementation in power plants and industrial facilities that burn fossil fuels, providing a highly effective method for reducing particulate and other harmful emissions, thereby mitigating environmental impact and supporting cleaner energy production.
-
Marine and Rail Transport: Application in large engines used in shipping and rail, sectors known for significant exhaust emissions. This technology could provide a compact and efficient solution for these mobile, heavy-duty applications.
-
Off-Road and Construction Equipment: Equipping heavy machinery used in construction, agriculture, and mining with this system would contribute to cleaner operations in demanding environments, reducing localized air pollution.
-
Industrial Processes: Utilization in various industrial processes that generate particulate-laden exhaust, such as manufacturing, chemical processing, and waste incineration, to meet environmental regulations and improve worker safety.
This patent presents an innovative and highly efficient solution for emission control, offering a compelling opportunity for licensees to integrate a next-generation particulate trap system into their products and operations, addressing a critical global need for cleaner ai