US 10,292,658
Apparatus, System, and Method for Medical Analyses of Seated Individual
Patent Number
Issue Date
Inventor(s)
David A. Borkholder; Nicholas J. Conn; Masoumeh Haghpanahi
Document
Download PDF for patent US 10,292,658Synopsis
Patent US 10,292,658 B2 describes an apparatus, system, and method for conducting medical analyses of an individual while seated. This invention provides a non-invasive and continuous way to monitor vital physiological parameters, such as ballistocardiograms (BCG), which reflect the mechanical forces generated by the heart's pumping action, and potentially other metrics like weight distribution.
The novel aspects of this invention lie in its discreet integration into a common household item, specifically a toilet seat, allowing for passive and repeated data collection.
Key innovations include:
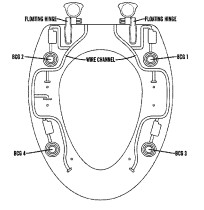
Integrated Sensing Platform: The system embeds multiple Ballistocardiogram (BCG) sensors within a toilet seat. These sensors are designed to detect minute movements and forces exerted by the body, which are directly related to cardiac activity. The placement on a toilet seat allows for a consistent posture and interaction with the sensors during regular, private use.
Contactless and Passive Monitoring: Unlike traditional medical devices that require conscious engagement or attachment, this system operates passively. An individual simply uses the toilet as normal, and data is automatically collected without any additional effort or discomfort. This unobtrusive nature encourages adherence to regular monitoring.
Physiological Data Acquisition: The BCG signals captured by the sensors can be analyzed to derive various cardiac parameters, including heart rate, heart rate variability (HRV), and potentially indicators of cardiovascular health or changes in cardiac function. The system can be configured with multiple BCG sensors, such as four sensors strategically placed on the seat, to capture comprehensive data.
Data Processing and Analysis: The patent describes a system capable of processing the raw BCG signals to extract meaningful physiological information. This can involve filtering, signal enhancement, and algorithms to derive health metrics.
Potential for Multifunctionality: Beyond BCG, the system may also integrate pressure sensors (e.g., load cells) to measure weight and its distribution, allowing for the potential assessment of fluid retention, gastrointestinal health, or changes in body composition over time.
The commercial potential of this invention is substantial, as it offers a seamless and highly accessible solution for continuous health monitoring within the domestic environment.
Possible applications include:
Remote Patient Monitoring: For individuals with chronic cardiac conditions (e.g., congestive heart failure, hypertension) or those at risk of cardiovascular events, this system could provide crucial daily insights to healthcare providers without requiring frequent clinic visits or the use of cumbersome wearables.
Elderly Care: In an aging population, discreet monitoring of vital signs is essential for maintaining health and independence. This technology could allow caregivers and family members to track the well-being of elderly individuals without intruding on their privacy.
Fluid Retention Management: By integrating weight monitoring capabilities, the system could assist in managing conditions like congestive heart failure, where daily weight fluctuations are critical indicators of fluid retention.
Sleep Apnea and Respiratory Monitoring: While primarily focused on cardiac activity, subtle movements related to breathing could potentially be captured, offering insights into respiratory patterns and sleep disorders.
Wellness and Preventive Health: For health-conscious consumers, the system could provide a simple way to track daily heart health trends, encouraging healthier lifestyle choices and early detection of potential issues.
Post-Operative Recovery: Patients recovering from cardiac surgery or other medical procedures could benefit from continuous, at-home monitoring to track their recovery progress and identify complications early.
This invention provides a compelling solution for discreet, continuous, and non-invasive health monitoring, uniquely leveraging a common daily activity to collect valuable physiological data. It presents a strong value proposition to potential licensees in the medical device, health technology, and smart home industries.