US 10,697,629
Devices with an Enhanced Boiling Surface with Features Directing Bubble and Liquid Flow and Methods Thereof
Synopsis
Patent US 10,697,629 B2 describes an innovative approach to enhance pool boiling heat transfer through precisely engineered surface features that actively manage the flow of vapor bubbles and liquid. The invention aims to overcome limitations of traditional boiling surfaces by preventing vapor blanketing, thereby increasing both the Heat Transfer Coefficient (HTC) and Critical Heat Flux (CHF).
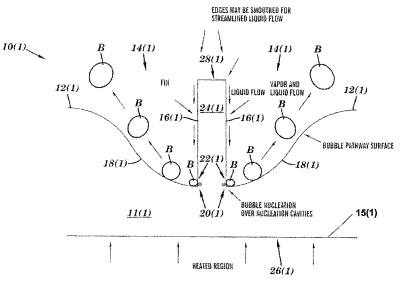
The core novelty of this patent lies in the creation of features on a heated surface that facilitate separate and optimized pathways for vapor bubbles departing the surface and fresh liquid approaching the surface.
This is achieved by designing specific geometries that:
Direct Vapor Flow: Structures on the surface guide newly formed vapor bubbles away from the heated surface and into the bulk liquid, preventing them from coalescing and forming an insulating vapor layer.
Promote Liquid Inflow: Simultaneously, these features create channels or pathways that actively draw fresh, cooler liquid towards the heated surface, ensuring continuous rewetting and efficient heat removal.
Optimized Surface Interaction: The interaction between the heated surface and the liquid is maximized, leading to more efficient bubble nucleation and departure, which are critical for high heat transfer rates.
This invention represents a significant advancement over passive surface enhancements (e.g., microfins, porous coatings) by actively controlling the two-phase flow dynamics at the microscale. By providing a dedicated mechanism for vapor removal and liquid replenishment, the system achieves higher heat fluxes before critical heat flux is reached, and sustains higher heat transfer coefficients.
The commercial potential of this technology is substantial across any industry where efficient thermal management is crucial.
Possible applications include:
Electronics Cooling: With the escalating power densities in CPUs, GPUs, data centers, and high-performance computing, conventional cooling methods are reaching their limits. This enhanced boiling surface could enable more compact, powerful, and reliable electronic devices by efficiently dissipating extreme heat loads.
Power Generation: In power plants (thermal, nuclear, concentrated solar), improving the efficiency of boilers, evaporators, and condensers translates directly into higher energy output and reduced fuel consumption. This technology could significantly enhance the performance of such heat exchangers.
Electric Vehicle and Battery Thermal Management: The efficient cooling of high-capacity battery packs and electric vehicle components is vital for their performance, longevity, and safety. This invention could provide a superior solution for maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
Industrial Process Heat Transfer: Many industrial processes, including chemical processing, refrigeration, and HVAC, rely heavily on efficient heat exchange. Implementing these enhanced surfaces could lead to more compact, energy-efficient, and cost-effective heat exchangers, reducing operational expenses and capital investment.
Aerospace and Defense: High-performance cooling is critical for advanced avionics, spacecraft, and military systems where weight, volume, and extreme thermal loads are key considerations. This technology offers a pathway to lighter and more powerful systems.
This invention provides a robust and scalable solution for achieving superior boiling heat transfer, making it a highly attractive proposition for licensees seeking to develop next-generation thermal management solutions.