US 10869722
METHOD AND FIXTURE FOR GUIDED PEDICLE SCREW PLACEMENT
Patent Number
Issue Date
Inventor(s)
Michael R. Caldwell; Mark W. Olles; Amit Singla
Licensed/Under Negotiation
Document
Download PDF for patent US 10869722Synopsis
Patent US 10,869,722 B2 describes a method and fixture for guided pedicle screw placement in spinal fixation, offering a customized, patient-specific approach to improve surgical accuracy and patient outcomes. The invention focuses on creating a combined template and implant designed for precise positioning of pedicle screws during spinal surgery.
The novel aspects of this invention lie in its comprehensive workflow and the integration of patient-specific data to create highly accurate surgical guides.
The method involves:
Image Data Acquisition and 3D Modeling: Scanning the patient's affected spinal segment to generate high-resolution image data, which is then processed into a detailed 3D model of the spine. This personalized anatomical representation is the foundation for subsequent steps.
Surgeon-Defined Screw Paths: A surgeon identifies and selects specific, optimal screw paths within the 3D model to best address the patient's unique condition. This ensures that the instrumentation is tailored to the individual patient's anatomy and pathology.
Digital Template Generation and Modification: Software is used to generate a digital template for a surgical fixture. This digital template is then precisely modified to align with the surgeon-selected screw paths.
Additive Manufacturing of Fixture: The customized fixture is fabricated from the finalized digital template using additive manufacturing (e.g., 3D printing). This allows for the creation of complex geometries that perfectly conform to the patient's spine.
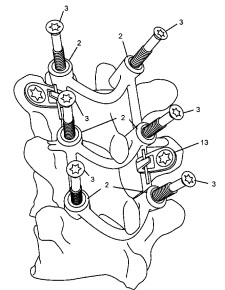
Guided Placement and Fixation: During surgery, the patient-specific fixture is precisely located on the affected spinal segment. It incorporates drill guides and screw passages through which drills and standard surgical screws are passed, ensuring accurate trajectory and depth. Once the drill depth is verified, the guide is removed, and the screws are placed. The fixture can also serve as a temporary implant or incorporate elements of the final implant.
The innovation significantly enhances surgical precision by eliminating reliance on less accurate freehand techniques or generic guides. By directly integrating patient anatomy and surgeon-planned trajectories into a physical guide, it minimizes the risk of malpositioning, potential nerve damage, or other complications. The ability to combine the template and a portion of the implant into a single, custom device further streamlines the surgical procedure.
The commercial potential for this invention is substantial within the orthopedic and neurosurgical fields, particularly in the rapidly expanding market for personalized medicine and precision surgery.
Possible applications include:
Spinal Fusion Procedures: This technology could become standard in complex spinal fusion surgeries (e.g., for scoliosis, degenerative disc disease, trauma), where accurate screw placement is critical for stability and successful outcomes. It could reduce operative time, improve patient recovery, and decrease revision rates.
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery (MISS): The precision offered by these custom guides is especially valuable in MISS, where limited visibility makes freehand techniques more challenging. The fixture could facilitate smaller incisions and less tissue disruption.
Revision Spine Surgeries: For patients undergoing revision surgery due to previous screw malposition or hardware failure, customized guides could provide the exact anatomical references needed to navigate complex, altered anatomy.
Training and Simulation: The 3D models and patient-specific guides could be invaluable for surgical planning, resident training, and simulating complex cases, allowing surgeons to practice specific procedures on accurate anatomical replicas.
This invention offers a compelling solution for improving the safety, efficacy, and efficiency of spinal fixation procedures. Its patient-specific nature, combined with the capabilities of advanced manufacturing, positions it as a transformative technology for surgical guidance systems, presenting a strong value proposition to potential licensees in the medical device industry.