US 108903777
VOLCANO-SHAPED ENHANCEMENT FEAURES FOR ENHANCED POOL BOILING
Synopsis
Patent US 10,890,377 B2 describes a system and method for significantly enhancing pool boiling heat transfer, a critical process for efficient heat removal in various applications. The invention introduces novel volcano-shaped enhancement features designed to optimize the flow dynamics of vapor and liquid during boiling, leading to improvements in both the Heat Transfer Coefficient (HTC) and the Critical Heat Flux (CHF).
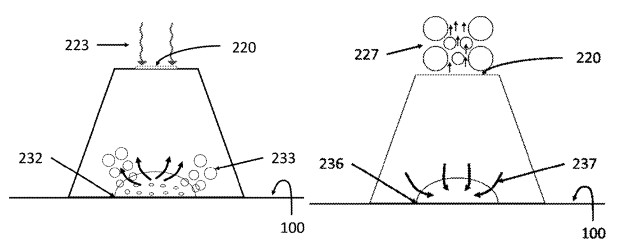
A key innovation of this patent lies in the unique geometry of the volcano-shaped structures. These structures are positioned on a heated substrate and are submerged in a liquid. Their design creates a contained volume between the structure and the substrate, with an opening at the base (or a gap) for liquid inflow and a top opening (or hole) for vapor expulsion. This configuration establishes a controlled, predominantly continuous flow pathway: vapor bubbles generated at the heated surface are efficiently directed out through the top opening, while fresh liquid is continuously drawn in through the base opening.
The novelty of this approach stems from its ability to mitigate common limitations in conventional pool boiling systems. By providing separate and well-defined pathways for vapor and liquid, the invention effectively reduces "vapor blanketing" or "agglomeration" at the heated surface. This ensures consistent rewetting of the heater surface by fresh liquid, which is crucial for sustaining high heat transfer rates and preventing premature dry-out, thereby increasing the CHF. Furthermore, the directed flow field reduces interference between departing vapor bubbles and incoming liquid, leading to a substantial improvement in the HTC. Experimental results demonstrate that these volcano-shaped structures can achieve enhanced heat flux and heat transfer coefficients compared to plain surfaces, even with varied top hole and base gap dimensions.
The commercial potential of this invention is substantial, as efficient heat removal is a pervasive challenge across numerous industries.
Possible applications include:
Electronics Cooling: With the ever-increasing power density of microprocessors, GPUs, and other electronic components, advanced cooling solutions are critical. This technology could enable more compact, reliable, and higher-performing electronic devices by efficiently dissipating large amounts of heat from chips and data centers.
Power Generation: In power plants, whether traditional thermal or advanced nuclear systems, efficient heat transfer is paramount for maximizing energy conversion efficiency and system stability. This technology could improve the performance of boilers, condensers, and other heat exchangers, leading to greater energy output and reduced operational costs.
Industrial Process Heating and Cooling: Many industrial processes, such as chemical reactions, distillation, and manufacturing, involve significant heat exchange. The enhanced boiling performance offered by these structures could lead to more compact and efficient heat exchangers, reducing energy consumption and capital expenditure.
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning: Improving the efficiency of evaporators in refrigeration and air conditioning systems could lead to significant energy savings and more environmentally friendly cooling technologies.
Thermal Management in Electric Vehicles and Batteries: The thermal management of high-power battery packs and electric vehicle components is vital for safety, longevity, and performance. This technology could offer a robust solution for maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
Aerospace and Defense: High-performance thermal management systems are essential for spacecraft, avionics, and defense applications where weight, volume, and extreme operating conditions demand highly efficient heat rejection.
The ability to significantly improve both the heat transfer coefficient and the critical heat flux makes this invention a compelling solution for next-generation thermal management systems. It offers the potential for smaller, more efficient, and more reliable heat exchange devices across a broad spectrum of industries, providing a competitive advantage to licensees.