11,100,397
METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR TRAINING MEMRISTIVE LEARNING SYSTEMS
Patent Number
Issue Date
Inventor(s)
Dhireesha Kudithipudi
Licensed/Under Negotiation
Document
Download PDF for patent 11,100,397Synopsis
Patent US 11,100,397 B2 describes a method and apparatus for training memristive learning systems. This invention addresses the challenges associated with efficiently and effectively training memristor-based neural networks, which hold significant promise for low-power, high-density artificial intelligence hardware. The conventional training methods often require complex external circuitry or suffer from limitations in handling the unique characteristics of memristors.
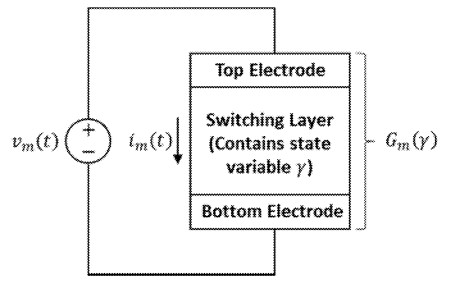
A key novel aspect of this patent is its approach to training memristive learning systems by adjusting memristance values based on a comparison between the system's output and a target output. The system utilizes a controller that generates a target output for a given input and then compares this target output to the actual output produced by the memristive learning system. Based on this comparison, the controller generates a "control signal" that is applied to the memristors. This control signal, which can be an electrical pulse (e.g., voltage or current pulse), modifies the memristance values in a way that reduces the difference between the actual and target outputs. The patent highlights the use of an "error correction" mechanism where the control signal is directly proportional to the difference between the expected and actual outputs, ensuring efficient and targeted adjustment of memristor states. This direct feedback loop enables effective training of complex neural network architectures implemented using memristors.
The commercial potential of this invention is substantial within the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence hardware. Memristor-based computing offers inherent advantages in power efficiency and computational density, making it a strong candidate for next-generation AI accelerators.
Possible applications include:
Edge AI Devices: Enabling highly efficient and low-power AI processing directly on edge devices such as smartphones, IoT sensors, drones, and autonomous vehicles. This reduces the need for constant cloud connectivity and improves real-time responsiveness for tasks like image recognition, natural language processing, and predictive maintenance.
Neuromorphic Computing: Accelerating the development of neuromorphic chips that mimic the structure and function of the human brain. This technology can contribute to creating more biologically plausible and energy-efficient AI systems capable of learning and adapting.
Data Centers and Cloud AI: Improving the energy efficiency and computational throughput of AI workloads in large-scale data centers. By offloading complex computations to specialized memristive hardware, power consumption can be significantly reduced while increasing processing speed for tasks like deep learning model training and inference.
Pattern Recognition and Signal Processing: Enhancing the performance of systems for real-time pattern recognition in various data streams, including audio, video, and sensor data. This is relevant for applications in security, surveillance, medical diagnostics, and industrial automation.
Machine Learning Accelerators: Providing a foundational technology for designing dedicated hardware accelerators for machine learning algorithms, offering significant performance improvements over traditional CPU/GPU architectures for specific AI tasks.
This patent offers a robust and adaptable training methodology for memristive learning systems, providing a pathway to unlock the full potential of memristor technology for developing next-generation, high-performance, and energy-efficient artificial intelligence hardware.