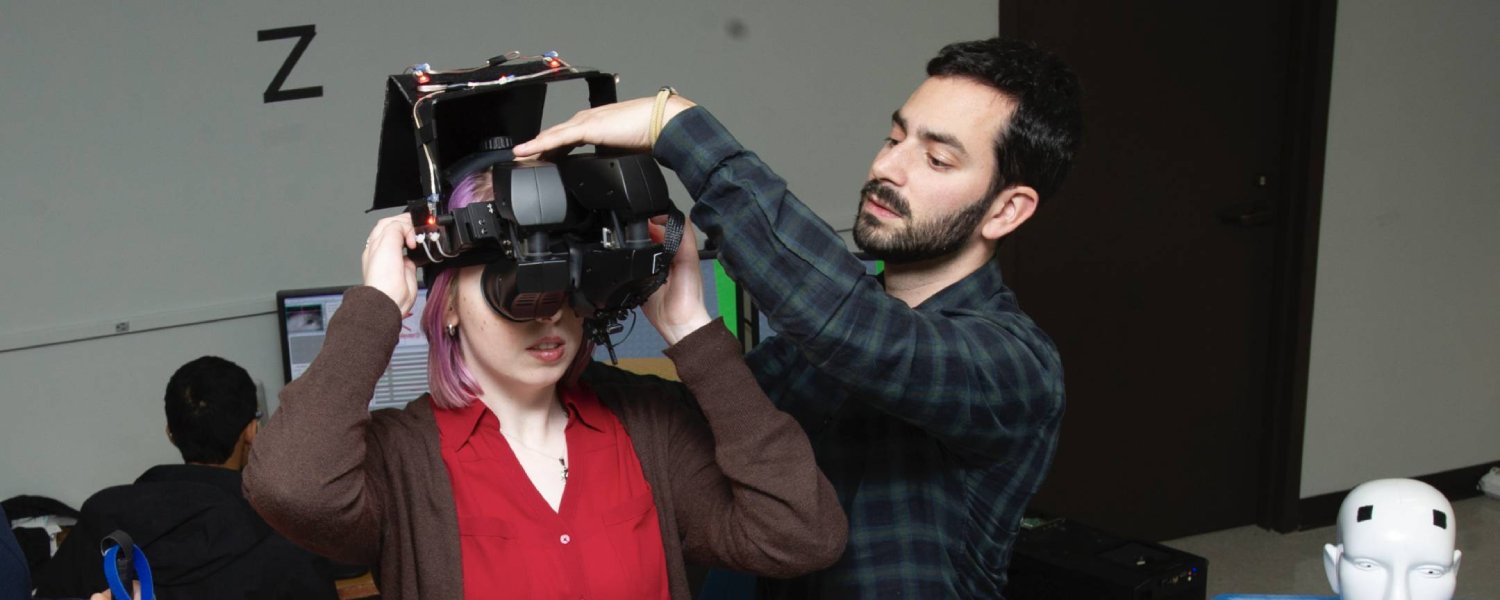
Imaging science is a unique major that combines math, physics, computer science, and engineering to develop imaging systems used in a wide array of industries.
When you hear the term imaging system you may think of an X-ray machine or other medical imaging such as MRI, mammography, or ultrasound. But as digital imaging has rapidly evolved, so have the many ways it can be used. Today, imaging systems monitor agriculture, study art, visualize architecture, protect and secure the nation, explore the universe, and drive cars.
Augmented reality. Environmental conservation. National defense. Self-driving cars. Learn about six jobs you’ll be competitive for with a bachelor’s degree in imaging science.
RIT’s imaging science degree has a 100% outcome rate. Graduates are employed at world-renowned companies such as Adobe, Amazon, Apple, Aptiva Imaging, Boeing, Google, L3 Harris, Lockheed Martin, NASA, National Geospatial Intelligence Agency, Naval Undersea Warfare Center, and more.
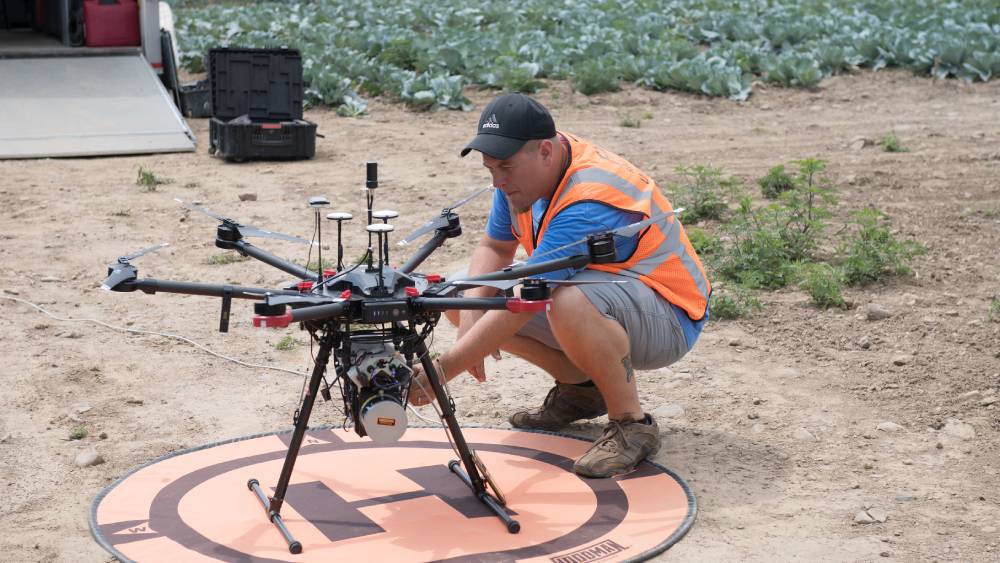
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (Drone) Engineer
When you think of drones you may think of military exercises or your local photographer’s website. But these devices are used extensively for business purposes. Drones are used by agricultural companies to monitor crops and track disease, by insurance agencies to document and assess damage after natural disasters, and by conservation organizations to monitor the environment. These imaging systems also can be combined with predictive analytics to improve our use of resources across all of these areas. An imaging science degree prepares students to develop and design the cameras, imaging types, and engineering techniques needed to ensure drones can not only carry advanced imaging cameras but can convert the large quantities of data they collect into useful information for the end-user.

Computer Vision Scientist
Nearly every automaker is developing or looking to enhance, their driver assistance systems by using computer vision technologies. These are the systems that deploy the brakes in an emergency or help you parallel park your car. Imaging science students learn math and programming skills needed to work on engineering teams that are utilizing RADAR, LIDAR, and other imaging systems in the pursuit of fully-autonomous vehicles and other new technologies. Computer vision systems are also used in cell phone cameras and the apps that run on them, AR/VR systems, medical image analysis, as well as in manufacturing systems.
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality Researcher
You could be on the team developing the next augmented reality experience for gamers, working with city planners to show 3D prototypes of a new skyline, or helping stroke victims regain their vision. AR/VR technologies are growing at a rapid pace and the demand for skilled imaging experts is high. An imaging science degree prepares students to work at many AR/VR companies developing the hardware and software systems that drive this technology forward. These careers require experience with programming languages, an understanding of human and computer vision, and the ability to design, conduct, and troubleshoot experiments.
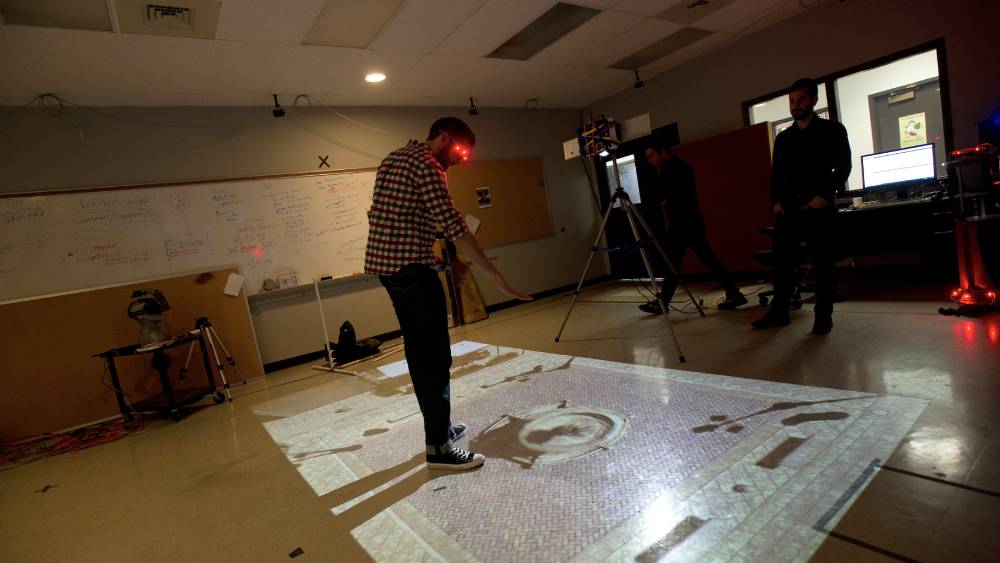

Satellite Imaging Scientist
Right now, more than 2,500 satellites are orbiting Earth. In 2017, Planet, an American satellite company, began snapping a daily picture of every part of Earth’s landmass. How are all these satellite images being used? NASA is constantly learning about the universe through satellite imagery while countries around the world use satellite imagery to ensure national security. Imaging scientists work at leading aerospace companies and national labs developing new imaging systems for satellites, as well as applying artificial intelligence algorithms to extract information from those images. These applications can range from environmental monitoring to national security and beyond.
Camera Hardware Engineer
Smartphone engineers are tasked with developing the tools of the future, like simultaneously developing smaller cameras with the highest image resolutions possible. Camera hardware engineers are involved in the research, design, development, testing, and qualification of camera hardware for new products. To succeed in this role, you need to understand image evaluation methodology and image quality metrics, have strong programming skills, and be familiar with imaging algorithms and objective camera bench testing. Very few college programs provide this level of diverse training in the way RIT’s imaging science degree does.
Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning Engineer
Artificial intelligence (AI) is when a machine responds to a stimulus the way a human might respond. One example you’re probably familiar with is tagging your photos on Facebook or Instagram. The only way a machine learns to respond in a certain way is through proper programming. An AI engineer builds models using machine learning algorithms and deep learning neural networks. To do this, these engineers often have a background in areas like computer science, mathematics, and cognitive science–all of which are areas covered in RIT’s imaging science degree. AI engineers are in demand in a range of industries including aerospace, agriculture, medicine, and the cell phone industry.