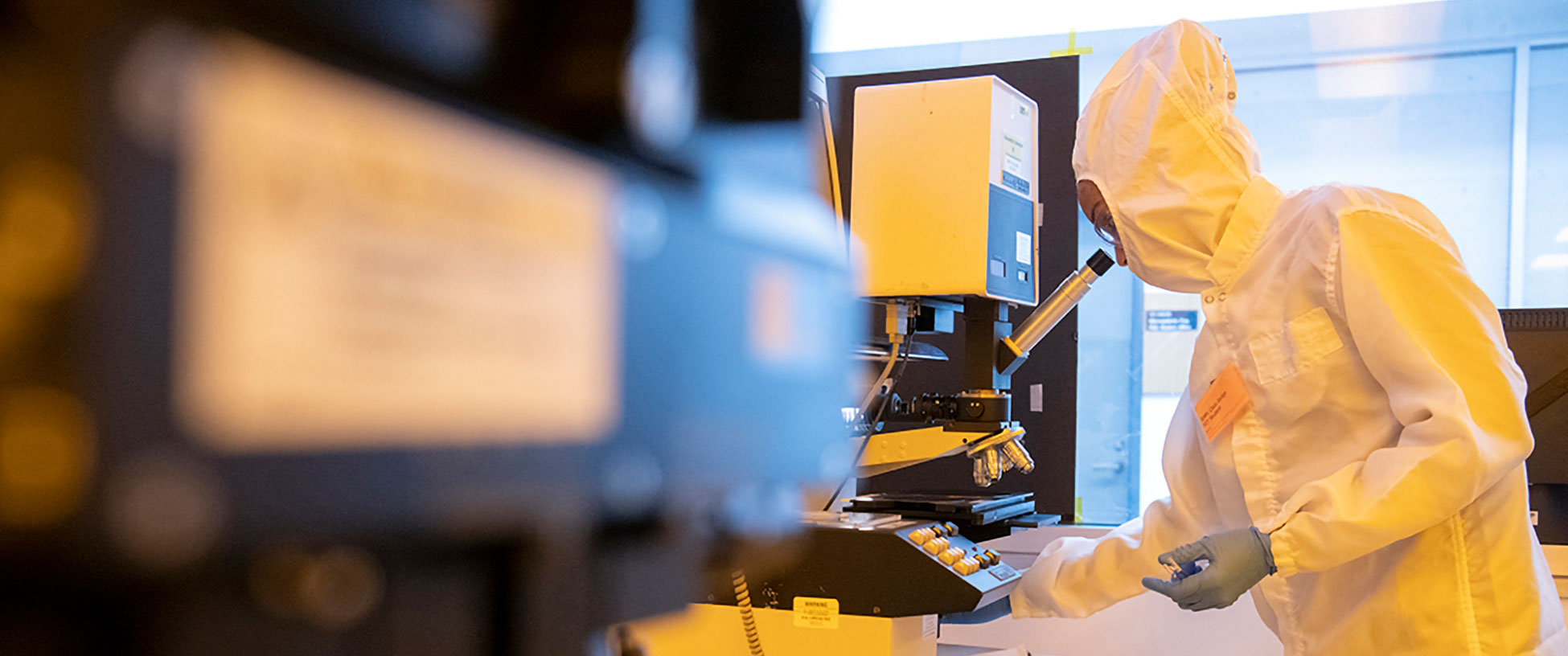
As technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, the field of microelectronics is becoming increasingly vital to many industries. A degree in microelectronic engineering offers graduates a diverse array of career paths, allowing them to engage in cutting-edge advancements that shape the future.
From semiconductor design to embedded systems development, microelectronics professionals play crucial roles in creating the devices and systems that drive modern life. Check out the hottest jobs in microelectronics right now:
- Semiconductor Process Engineer: Working on the fabrication processes of semiconductor devices, ensuring the efficiency, reliability, and quality of semiconductor manufacturing processes.
- Semiconductor Device Engineer: Overcome the limitations of miniaturization by implementing new solutions in materials and device structures for continuous improvements in packing density, switching speed, and power consumption.
- Integrated Circuit (IC) Design Engineer: Designing and developing microchips and integrated circuits for various applications such as computer processors, memory chips, and sensors.
- Embedded Systems Engineer: Working on the design, development, and testing of embedded systems for applications like consumer electronics, automotive systems, medical devices, and industrial control systems.
- Analog or Digital Circuit Design Engineer: Specializing in designing analog or digital circuits for specific applications such as signal processing, power management, or communication systems.
- Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS) Engineer: Designing and developing miniature mechanical and electrical devices, such as sensors and actuators, for various applications, including biomedical devices, consumer electronics, and automotive systems.
- Product Development Engineer: Developing new electronic products by integrating microelectronics components into innovative designs, overseeing the entire product development lifecycle from concept to production.
- Research and Development (R&D) Engineer: Conducting research to explore new technologies, materials, and techniques for improving microelectronics devices and systems.
- Quality Assurance Engineer: Ensuring the quality and reliability of microelectronics products through testing, analysis, and optimization of manufacturing processes.
- Technical Sales Engineer: Providing technical expertise and support to customers, marketing teams, and sales personnel for microelectronics products and solutions.
- Academic or Research Scientist: Pursuing advanced studies and research in microelectronics, contributing to advancements in the field through academic research, teaching, and publications.
A career in microelectronics not only promises exciting job prospects but also the chance to be at the forefront of technological innovation. As industries continue to seek professionals skilled in microelectronics, graduates can expect a dynamic work environment that encourages creativity and problem-solving. Whether working on the design of next-generation microchips or developing new electronic products, the roles within this field are both impactful and rewarding. For those considering a degree in microelectronic engineering, the future is bright, filled with opportunities to contribute to advancements that will shape our world.