Computer Science Bachelor of Science Degree

Computer Science
Bachelor of Science Degree
- RIT /
- Rochester Institute of Technology /
- Academics /
- Computer Science BS
Specialize in AI, robotics, cybersecurity, graphics, and more with RIT’s flexible and powerful computer science degree.
Overview for Computer Science BS
Why Study Computer Science at RIT?
Personalize Your Degree: Explore various areas within computer science, from artificial intelligence to computer security, tailoring your education to match your interests and career goals.
Comprehensive Skill Development: Gain proficiency not only in programming but also in problem-solving, analytical reasoning, and effective communication, essential qualities sought after by employers in today’s competitive job market.
Hands-On Learning Opportunities: Engage in significant programming, software development, and research projects, allowing you to apply theoretical concepts to real-world challenges and develop practical expertise.
Interdisciplinary Approach: Immerse yourself in a holistic educational experience, integrating mathematics, science, liberal arts, and technical skills, preparing you to excel in diverse career paths within the rapidly evolving field of computer science.
Accelerated Bachelor’s/Master’s Available: Earn both your bachelor’s and your master’s in less time and with a cost savings, giving you a competitive advantage in your field.
STEM-OPT Visa Eligible: The STEM Optional Practical Training (OPT) program allows full-time, on-campus international students on an F-1 student visa to stay and work in the U.S. for up to three years after graduation.
Computer science covers a wide spectrum of areas within the field of computing, ranging from theoretical to practical. As a computer scientist, you can specialize in areas such as intelligent systems (i.e., artificial intelligence), computer graphics, computer theory, data management, distributed and parallel computing, systems software, or computer security.
While programming is necessary, computer scientists must also be adaptable and adept at problem-solving and analytical reasoning, able to understand design principles, mathematical theory, and fluent technical applications of computer science. RIT prepares you to be well versed in all these aspects including programming because most employers look for students who are good computer scientists, but also understand the tools and techniques of mathematics, science, and industry, and are able to communicate effectively.
RIT’s Computer Science Degree
You will take a core of computer science courses that provide a solid foundation for advanced work. Building on this base, explore a variety of specializations in your third, fourth, and fifth years. In addition, you will develop a broad appreciation for computer applications and the effect of computers on society via program electives, general education courses, and various free electives, which can be used to complete a minor.
The computer science bachelor’s degree provides you with both a broad and deep foundation in theory and modern software and hardware concepts as well as introduces you to numerous programming languages and paradigms. RIT offers you the opportunity to engage in significant programming and software development work, or in both traditional and applied research.
In addition to required computer science BS courses, you may take computer science electives in areas such as architecture and operating systems; computer graphics and visualization; data management; distributed systems; artificial intelligence; languages and tools; security; and theory.
Students who graduate from our computer science degree are able to:
- Analyze a complex computing problem and apply principles of computing and other relevant disciplines to identify solutions.
- Design, implement, and evaluate a computing-based solution to meet a given set of computing requirements in the context of the program’s discipline.
- Communicate effectively in a variety of professional contexts.
- Recognize professional responsibilities and make informed judgments in computing practice based on legal and ethical principles.
- Function effectively as a member or leader of a team engaged in activities appropriate to the program’s discipline.
- Apply computer science theory and software development fundamentals to produce computing-based solutions.
- Demonstrate advanced knowledge of a selected area within the computer science discipline.
Careers in Computer Science
Employers not only look for students who have strong technical skills, but who also understand mathematics, science, and the importance of effective communication. The computer science degree provides students with a solid foundation in mathematics, science, liberal arts and an opportunity to take outside electives, complementing the program's strong technical core.
Furthering Your Education in Computer Science
Combined Accelerated Bachelor’s/Master’s Degrees
Today’s careers require advanced degrees grounded in real-world experience. RIT’s Combined Accelerated Bachelor’s/Master’s Degrees enable you to earn both a bachelor’s and a master’s degree in as little as five years of study, all while gaining the valuable hands-on experience that comes from co-ops, internships, research, study abroad, and more.
- Computer Science BS/MS: Combine a computer science BS degree with an MS degree in computer science to prepare for careers in the rapidly growing and ever-changing field of computing. Start by gaining proficiency in programming as well as problem-solving, analytical reasoning, and effective communication, essential qualities sought after by employers in today’s competitive job market. You’ll specialize in areas such as artificial intelligence, computer graphics, computer theory, networking, security, robotics, parallel computation, data mining, computer architecture, or systems software. Then, during your graduate course work you’ll tailor your degree to your interests including selecting a cluster of computer science courses that will help you reach your goals in a career you love. Some graduates pursue further education earning a Ph.D.
- Computer Science BS/Cybersecurity MS: The BS/MS pathway in computer science and cybersecurity offers students a dynamic combination of broad computing knowledge and specialized security expertise. The BS in computer science lays a strong foundation in core computing principles, while the MS in cybersecurity provides in-depth training in digital defense strategies and securing systems. Through hands-on experience in state-of-the-art facilities like our Cyber Range, including executing penetration tests and vulnerability assessments, students gain practical skills highly valued by employers. Graduates of this accelerated program are uniquely positioned to become leaders in the high-demand, high-growth field of cybersecurity, with opportunities spanning from corporate IT security to government intelligence agencies.
- Computer Science BS/Software Engineering MS: The BS/MS pathway in computer science and software engineering offers students a powerful blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application. The BS in computer science provides a broad foundation in computing, including areas like artificial intelligence and computer graphics. This is complemented by the MS in software engineering, which hones students' abilities in large-scale software development and innovation. This unique combination prepares graduates for leadership roles in the tech industry, from startups to major corporations. Through the program's focus on both traditional and applied research, students learn to not only use existing technologies but also to invent new ones. The accelerated timeline allows students to quickly position themselves at the forefront of software development, equipping them with the advanced skills and experience that employers highly value in today's rapidly evolving tech landscape.
- +1 MBA: Students who enroll in a qualifying undergraduate degree have the opportunity to add an MBA to their bachelor’s degree after their first year of study, depending on their program. Learn how the +1 MBA can accelerate your learning and position you for success.
-
#54 Best Computer Science Undergraduate Programs, 2026
RIT’s computing majors are ranked among the Best Undergraduate Computer Science Programs nationally.
-
Apply for Fall 2026
First-year students can apply for Early Decision II by Jan. 1 to get an admissions and financial aid assessment by mid-January.
Careers and Cooperative Education
Typical Job Titles
| Associate Software Engineer | Automation Engineer | Developer |
| Full Stack Developer | Programmer/Analyst | QA Test Engineer |
| Senior Software Engineer | Software Developer | Software Engineer |
| Technology Analyst |
Industries
-
Defense
-
Electronic and Computer Hardware
-
Health Care
-
Internet and Software
-
Research
-
Financial Services
Cooperative Education
What’s different about an RIT education? It’s the career experience you gain by completing cooperative education and internships with top companies in every single industry. You’ll earn more than a degree. You’ll gain real-world career experience that sets you apart. It’s exposure–early and often–to a variety of professional work environments, career paths, and industries.
Co-ops and internships take your knowledge and turn it into know-how. Your computing co-ops will provide hands-on experience that enables you to apply your computing knowledge in professional settings while you make valuable connections between classwork and real-world applications.
Students in the computer science degree are required to complete three blocks of cooperative education experience.
Featured Work and Profiles
-
Coding Meets Capital: RIT Co-op Student Innovates in Financial Tech Startup
Ben McManus, a fifth-year computer science student, gained firsthand experience in automation and IT in his co-op at Indivisible Partners, a national startup finance company.
Read More about Coding Meets Capital: RIT Co-op Student Innovates in Financial Tech Startup -
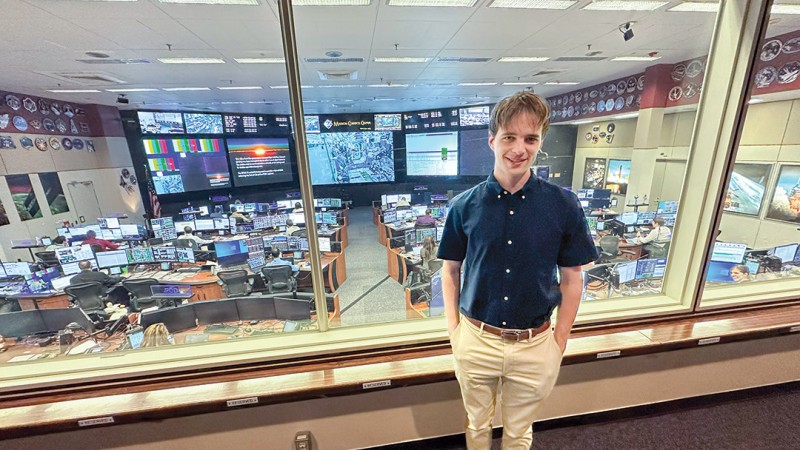
Co-op Program Leads Student to NASA Opportunity
Conor Gagliardi ‘25 secured a prestigious co-op at NASA's Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center where he programs autonomous rovers and contributes to NASA’s SUITS Challenge framework.
Read More about Co-op Program Leads Student to NASA Opportunity -
RIT Alumnus Named to Forbes 30 Under 30 for Gaming Innovation
Through the company that he co-founded while in college, McDonald is now making it easier for millions of people to play and explore in the video game Minecraft.
Read More about RIT Alumnus Named to Forbes 30 Under 30 for Gaming Innovation -
Exploding Kittens Game Created by RIT Alumnus Debuts on Netflix
Read More about Exploding Kittens Game Created by RIT Alumnus Debuts on Netflix -
What's Being Made in the SHED
Making at RIT has hit a new level now that several makerspaces in the Student Hall for Exploration and Development (SHED) have opened. Learn what's being created.
Read More about What's Being Made in the SHED -
Machine Learning Meets Law Enforcement in RIT Research Project
RIT twins Angela and Anita Srbinovski join a $1M study using statistical machine learning to analyze police body-camera footage to help improve officer training.
Read More about Machine Learning Meets Law Enforcement in RIT Research Project
Curriculum for 2025-2026 for Computer Science BS
Current Students: See Curriculum Requirements
Admissions and Financial Aid
This program is STEM designated when studying on campus and full time.
First-Year Admission
First-year applicants are expected to demonstrate a strong academic background that includes:
- 4 years of English
- 3 years of social studies and/or history
- 4 years of mathematics is required and must include algebra, geometry, algebra 2/trigonometry, and pre-calculus. Calculus is preferred.
- 2-3 years of science is required and must include chemistry or physics; both are preferred.
- Computing electives are preferred.
Transfer Admission
Transfer applicants should meet these minimum degree-specific requirements:
- A minimum of precalculus is required. Calculus is preferred.
- Chemistry or physics is required.
- Computing courses are preferred.
Financial Aid and Scholarships
100% of all incoming first-year and transfer students receive aid.
RIT’s personalized and comprehensive financial aid program includes scholarships, grants, loans, and campus employment programs. When all these are put to work, your actual cost may be much lower than the published estimated cost of attendance.
Learn more about financial aid and scholarships
Accreditation
Related News
-
December 2, 2025

Students go Into the ROC to connect with their community
Through Into the ROC, a program that introduced nearly 8,500 RIT community members to the region since 2016, students have explored, volunteered, and built lasting community ties.
-
November 24, 2025

RIT partners with Gallaudet University to launch research traineeship program in Universal AI
RIT is teaming up with Gallaudet University to prepare the next generation of artificial intelligence researchers and practitioners who will develop AI for everyone.
-
November 20, 2025

Cross-disciplinary collaborations lead to growth for double-major students
From satellite debris to artificial intelligence, double major students find research success by combining expertise in computer science and economics.
Contact
- Dukka KC
- Department Chair
- Department of Computer Science
- Golisano College of Computing and Information Sciences
- 585‑475‑2840
- dkcvcs@rit.edu
Department of Computer Science