Project Fast Forward
Contact
David Strom, Director
Phone: (585) 270-0544 (VP)
fastforward@rit.edu
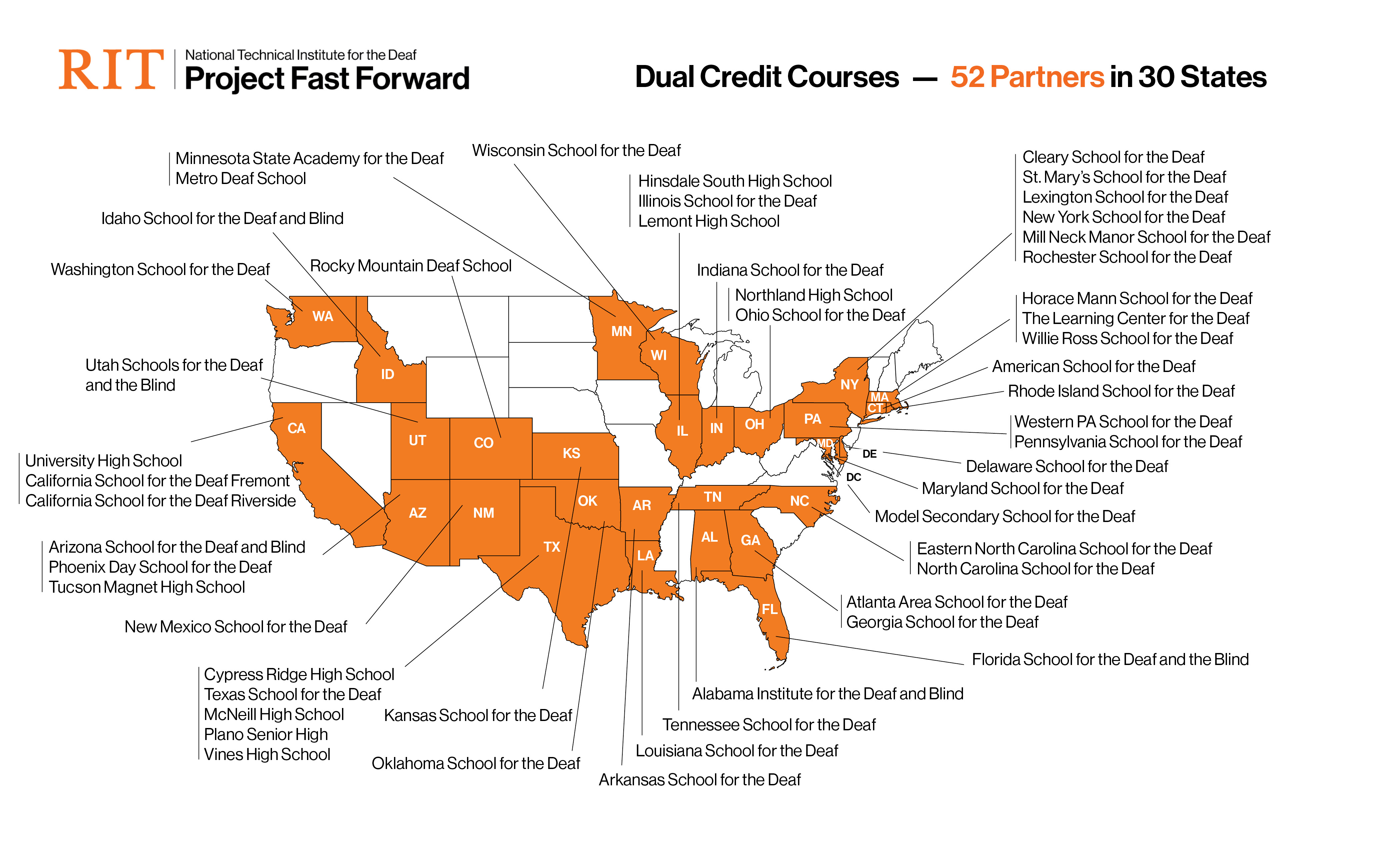
52
Partnerships
Dual-credit partnerships with high schools in 30 states across the country
24
Courses
RIT/NTID dual-credit courses offered
2k+
Students
Deaf and hard-of-hearing high school students who have completed RIT/NTID dual-credit courses
200+
Trained
Teachers, counselors, and administrators who are trained in administering RIT/NTID dual-credit courses
Deaf and hard-of-hearing students can get a jump start on their college journey.
Project Fast Forward helps deaf and hard-of-hearing high school students across the country get a jump start on a college degree by offering dual-credit college courses in STEM (science, technology, engineering, and math) areas. The ultimate goal of the program is to inspire deaf and hard-of-hearing students' interest in STEM careers and for students to gain introductory skills in STEM fields while earning college credit.
The dual-credit courses are offered by Rochester Institute of Technology’s National Technical Institute for the Deaf. The courses are taught at the students’ high schools, by their own teachers, during regular school hours. Courses are offered in schools after a teacher undergoes professional development training at RIT/NTID (view School Information for details). The credits earned by students can be used toward a degree at RIT/NTID or any other college across the country that accepts the credit.
Teachers, counselors, and school administrators who are involved with Project Fast Forward receive:
- Covered travel, lodging, and meal expenses associated with professional development training held for three days during the summer on the RIT campus, with eligibility for a stipend.
- Training in secondary education at RIT/NTID, including insights into today's world of STEM careers from RIT/NTID employment specialists, and strategies for connecting with and educating deaf and hard-of-hearing students.
- Access to Project Fast Forward award funds, which cover instructional costs and supplies for dual-credit courses (see PFF Award for more details.)

Summer 2024 New PFF Teacher/Counselor Cohort
Project Fast Forward Partner High Schools
52 Partners: in 30 states
| Alabama | Alabama Institute for the Deaf and Blind |
| Arkansas | Arkansas School for the Deaf |
| Arizona | Arizona School for the Deaf and Blind Phoenix Day School for the Deaf Tucson Magnet High School |
| California | California School for the Deaf Fremont California School for the Deaf Riverside University High School |
| Colorado | Rocky Mountain Deaf School |
| Connecticut | American School for the Deaf |
| Delaware | Delaware School for the Deaf |
| District of Columbia | Model Secondary School for the Deaf |
| Florida | Florida School for the Deaf and Blind |
| Georgia | Atlanta Area School for the Deaf Georgia School for the Deaf |
| Idaho | Idaho School for the Deaf and Blind |
| Illinois | Hinsdale South High School Illinois School for the Deaf Lemont High School |
| Indiana | Indiana School for the Deaf |
| Kansas | Kansas School for the Deaf |
| Louisiana | Louisiana School for the Deaf |
| Maryland | Maryland School for the Deaf |
| Massachusetts | Horace Mann School for the Deaf The Learning Center for the Deaf Willie Ross School for the Deaf |
| Minnesota | Metro Deaf School Minnesota State Academy for the Deaf |
| New Mexico | New Mexico School for the Deaf |
| New York | Cleary School for the Deaf Lexington School for the Deaf Mill Neck Manor School for the Deaf New York School for the Deaf Rochester School for the Deaf St. Mary's School for the Deaf |
| North Carolina | Eastern North Carolina School for the Deaf North Carolina School for the Deaf |
| Oklahoma | Oklahoma School for the Deaf |
| Ohio | Northland High School Ohio School for the Deaf |
| Pennsylvania | Pennsylvania School for the Deaf Western PA School for the Deaf |
| Rhode Island | Rhode Island School for the Deaf |
| Tennessee | Tennessee School for the Deaf |
| Texas | Cypress Ridge High School McNeil High School Plano Senior High Texas School for the Deaf Vines High School |
| Utah | Utah Schools for the Deaf and the Blind |
| Washington | Washington School for the Deaf |
| Wisconsin | Wisconsin School for the Deaf |
Student Information
- Are you curious about STEM careers?
- Are you considering your plans after high school?
- Do you want to experience college-level course work?
- Do you enjoy project-based learning?
- If you answered “yes” to any of the above, then this dual-credit opportunity is for you! Read on.
- Eases your transition from high school to college.
- Learn how to study for college courses and develop the skills needed to be successful in college such as:
- Following a syllabus
- Meeting course requirements
- Organizing and managing time effectively
- Using self-discipline
- Improving and applying high-level thinking skills
- Following college course policies and procedures
- Gain the confidence you need to succeed in college.
- Explore STEM careers.
- Earn free college credit while you are still in high school.
- Be considered for scholarships exclusively for Project Fast Forward students when you enroll at RIT/NTID.
There is no cost associated with enrolling in an RIT/NTID dual-credit course and receiving college credit.
Dual-credit courses are established by an agreement between the high school and the college. Enrollment in a dual-credit course requires that you satisfy both the college and high school eligibility requirements. After you complete the course you receive a final grade for the course and the college credit earned from the college. In contrast, Advanced Placement (AP) is a national standardized program where you must only meet high school eligibility requirements to enroll in an AP course and take an optional exam to earn AP credit.
Having RIT credits does not guarantee that you will be accepted into a program, even at RIT. All colleges and universities establish their own policies for accepting credits and those decisions are based on many factors.
Most often, these credits are counted as ‘free’ electives, not only at RIT but also should they be accepted at another college or university. It is important for you to check with your prospective colleges/universities as to whether or not the credit is accepted.
If you have completed a Project Fast Forward course and are interested in applying to colleges, including RIT, you may request a transcript be sent to those schools. Transcripts must be requested electronically and there is a fee for each transcript.

Ashely Locatelli
California School for the Deaf, Fremont
My dual-credit class introduced me to the rigors of college course work and taught me problem-solving skills that I could apply to my class assignments.

Flavio Medina, Jr.
Model Secondary School for the Deaf
I enjoyed taking a dual-credit class in high school because it gave me an opportunity to explore my interests early on and find my passion.
School Information
- PFF is the first dual-credit program focusing on deaf and hard-of-hearing students and is the leading effort in this area. Be a part of the future.
- Your students will receive an enriching experience; get hands-on learning opportunities; improve their discourse, analysis, and critical-thinking skills; and expand other important skills that are hallmarks of a college education experience.
- Your students learn how to study for college-level courses.
- Your students prove they can do college-level work.
- Your students develop the confidence they need to succeed in college.
- Your students have the opportunity to explore STEM careers.
- Your students earn free college credit while they are still in high school.
- You will meet and network with other professionals in your field.
- You will learn from a Deaf and/or ASL fluent professional in your academic area.
- You will expand your knowledge and skill set.
- You will have the opportunity to serve as a mentor to other high school teachers who teach the same dual-credit course.
- You will become a part of a community of dual-credit educators.
Have your school administrator contact Project Fast Forward at fastforward@rit.edu to express your school’s interest in establishing a dual-credit partnership.
Project Fast Forward, through RIT/NTID and the NTID Regional STEM Center, covers travel, lodging, and meal expenses associated with professional development training for high school teachers, administrators, and counselors. Deaf and hard-of-hearing high school students may register for RIT/NTID dual-credit courses and receive college credit at no cost, except for a small fee when ordering an RIT transcript.
Deaf and hard-of-hearing students who show enthusiasm for learning, solving complex problems, engaging in dialogue, and pursuing inquiry are encouraged to enroll in an RIT/NTID dual-credit course. Other potential indicators include:
- Satisfying high school requirements such as:
- GPA
- Grades in previous subject-area courses
- Test scores
- Course/credit hour limitations
- Postsecondary transition goals
- Being recommended by a high school teacher and/or guidance counselor
- Check Registration for other characteristics in a student candidate
Teachers attend summer professional development training at RIT for three days to prepare to teach dual-credit courses at their high school. Project Fast Forward covers all travel, lodging, and meal expenses. Participants who complete the Project Fast Forward training are eligible for at least .5 hours of CEU credit and also may receive a stipend. This year's training will be held the week of June 22, 2026 with virtual training options that can be coordinated on a flexible schedule for experienced teachers.
Before the training, teachers complete a survey about the specific topics they need to learn, allowing for tailored professional development. Course materials are provided before, during, and after the training.
The summer training includes:
- Technical training on course content and teaching methodologies.
- Information on Project Fast Forward, dual-credit course agreements, and course objectives and requirements.
Each summer, Project Fast Forward offers professional development at RIT for school administrators and high school counselors. Like teachers, administrators and counselors attend for three days, and travel, lodging, and meal expenses are covered. They also are eligible for a stipend.
The training includes:
- Information on Project Fast Forward, dual-credit course agreements, and course content, objectives and requirements.
- Discussions about post-secondary transition planning resources and strategies to support students through their transition.
Courses
The following RIT/NTID courses will be available for dual credit during the 2026-2027 school year.
PDF version of the courses and descriptions (open your PDF viewer sidebar to show the outline/table of contents for easy navigating to courses.)
Business Studies
Course Number NACC-130 Credits 3
Instructor: Kathleen Brady
This course provides students with information and resources needed to understand the creation and implementation of a budget, use of credit and borrowing money responsibly, financial rights and ways to safeguard their money, and factors used to determine their readiness to buy a home or make other major purchases. Information on financial institutions such as banks, credit unions, and savings and loan organizations will also be covered. This course will provide students with basic financial literacy so they can develop sound financial management of their personal income as well as an understanding of the economic events that can influence their financial well being and society as a whole.
Goals
- To develop technical reading and writing skills as well as problem solving, critical thinking and decision-making skills related to understanding various financial aspects of everyday life
- To develop short-term and long-term financial goals required for a personal budget plan.
- To develop an understanding of banking services and credit usage
- To develop an appreciation of sound personal financial management
- To develop an understanding of various decision-making processes that applies to the roles of citizens, workers, and consumers
Topics
- Personal Decision Making
- Paychecks
- Earning and Reporting Income
- Banking and Financial Institutions
- Saving and Investing
- Higher Education: Investment and Expenditures
- Managing Finances and Budgeting
- Buying Goods and Services
- Protection Against Risk
- Using Credit
- Retirement Planning
- Estate Planning
Learning Outcomes
| Outcome: At the completion of this course, students will be able to: |
Assessment Method |
|---|---|
|
Instructor Observation, Homework Assignments, Exams, and In-Class Activities |
|
Instructor Observation, Homework Assignments, Exams, and In-Class Activities |
|
Homework Assignments and In-Class Activities |
|
Instructor Observation, Homework Assignments, Quizzes, Exams, and In-Class Activities |
|
Assignments, Quizzes, Exams, and In-Class Activities |
Required Textbooks
- PFIN, 7th Edition, Randall Billingsley, Lawrence Gitman, and Michael Joehnk. Cengage, 2020
- The Infographic Guide to Personal Finance: A Visual Reference for Everything You Need to Know, Michael Cagan and Elisabeth Lariviere. Simon & Schuster, Inc., 2017
ISBN: 9781507204665
Other Required Materials
- Computer Lab with connections to online services and media projection equipment
- Microsoft Office software (i.e., microsoft.com/money)
- Intuit software (i.e., Quicken and TurboTax)
- World Wide Web/Internet personal finance sites (i.e., money.cnn.com, kiplinger.com, mymoney.gov, and mint.com)
Course Number NAST-160 Credits 3
Instructor: Bakar Ali
Emphasis will be on creating, formatting, and enhancing worksheets; creating and applying formulas and functions; building and formatting charts; using What-If analysis and creating templates. Upon completion, students will be able to design and enhance basic spreadsheets.
Goals
- To develop a strong foundation in the fundamental concepts and terminology used in the design and development of data in a spreadsheet
- To provide an understanding of how spreadsheet applications incorporate communication skills, information management skills and the ability to work without direction as required on the job
- To develop the technical reading and writing as well as critical thinking decision-making and problem-solving skills needed to analyze and manipulate data in a spreadsheet
- To develop appropriate work skills by modeling appropriate business behaviors and attitudes in the classroom
Topics
- Organizing and analyzing data
- Creating a worksheet
- Formatting data and content
- Managing data and workbooks
- Creating and applying formulas and functions
- Creating and formatting charts
- Applying What-If analysis
- Collaborating
- Creating templates and customizing spreadsheets
Learning Outcomes
| Outcome: At the completion of this course, students will be able to: | Assessment Method |
| 1. Develop a strong foundation in the fundamental concepts and terminology used in the design and development of data in a spreadsheet. (Goal 3.1) 1.1 Defines technical terminology 1.2 Designs and develops spreadsheets by organizing, analyzing and creating data in a worksheet; formatting data and content while managing data and workbooks; creating and formatting charts in a professional manner; creating templates and customizing worksheets |
Assignments, Exams |
| 2. To provide an understanding of how spreadsheet applications incorporate communication skills, information management skills and the ability to work without direction as required on the job 2.1 Demonstrates effective written communication through collaborative work 2.2 Demonstrates information management skills related to maintaining integrity of the spreadsheet 2.3 Demonstrates ability to work without direction |
Assignments, Exams |
| 3. To develop the technical reading and writing as well as critical thinking decision-making and problem-solving skills needed to analyze and manipulate data in a spreadsheet 3.1 Applies critical thinking and problem-solving skills to Determine relevant and correct information in a worksheet by creating and applying appropriate formulas; creating and applying appropriate functions; applying What-If Analysis 3.2 Applies technical reading comprehension to written questions about spreadsheets and its function in business |
Assignments, Exams |
| 4. Continue to develop appropriate work skills by modeling appropriate business behaviors and attitudes in the classroom 4.1 Model appropriate self-management while in the classroom by: 4.1.1 Demonstrating promptness 4.1.2 Utilizing all appropriate course materials 4.1.3 Meeting established deadlines 4.1.4 Managing stressful situations effectively while interacting with peers and faculty |
Mid-term/final exams, work skills evaluation form |
Required Textbooks
- New Perspectives Microsoft® Office 365® & Excel® 2019 Comprehensive , 1st Edition
Patrick Carey
ISBN-13: 978-0-357-70003-7
Other Required Materials
- Technology requirements:
- Regular and frequent access to a computer that is 0 - 5 years old, with at least 1GB of RAM
- Reliable high-speed internet access (broadband, cable, or fiber)
- An up-to-date web browser (Safari, Chrome, Internet Explorer, or Firefox)
- Microsoft Windows (Vista, 7 or later) or Mac OS X
- Able to print documents
- Able to record yourself and upload video posts/assignments
- Additional requirements as noted in course syllabus or as specified by instructor
- Access to a cloud/google drive
- Computer Lab with connections to online services and media projection equipment
- Microsoft 365
- Webcam with MP4 video capability
Course Number NBUS-200 Credits 3
Instructor: Adrianna Smart
This course introduces students to a broad overview of the form and structure of multinational organizations. It provides students with a basic knowledge of the history, organization and operation of business and its particular vocabulary.
Goals
- Develop technical reading, writing, problem solving, critical thinking, and decision-making skills related to basic business concepts. To develop short-term and long-term financial goals required for a personal budget plan
- Acquire knowledge of business ethics and social responsibility and examine their importance
- Acquire knowledge of global business climate, cross-cultural and international business and management practices
- Develop interpersonal and effective communication skills through appropriate interactions with peers, faculty, and guest speakers
Topics
- The Dynamics of Business and Economics
- Business Ethics and Social Responsibility
- Business in a Borderless World
- Managing Information Technology and E-Business
- Options for Organizing Business
- Small Business, Entrepreneurship, and Franchising
- The Nature of Management
- Organization, Teamwork, and Communication
- Managing Service and Manufacturing Operations
- Motivating the Workforce
- Managing Human Resources
- Customer-Driven Marketing
- Dimensions of Marketing Strategy
- Accounting and Financial Statements
- The Nature of Accounting
- The Accounting Process
- Financial Statements
- Money and the Financial System
- Money in the Financial System
Learning Outcomes
| Outcome: At the completion of this course, students will be able to: | Assessment Method |
| 1. Develop technical reading, writing, problem solving, critical thinking, and decision making skills related to basic business concepts (Goal 3.1) 1.1 Define technical vocabulary 1.2 Describe business concepts and applications using appropriate vocabulary |
Class assignments, quizzes, examinations Team presentations, class assignments, quizzes, class activities and examinations |
| 2. Acquire knowledge of business ethics and social responsibility and examine their importance. (Goal 3.2) 2.1 Draw conclusions on ethical dilemmas 2.2 Identify ways that organizations can act responsible to society |
Class activities, class assignments, projects Class assignments, quizzes, class activities and examinations |
| 3. Acquire knowledge of global business climate, cross-cultural and international business and management practices. (Goal 3.3) | |
| 3.1 Identify the major barriers that confront global businesses. | Team presentations, class assignments, quizzes, class activities and examinations |
| 3.2 Identify the types of trade restrictions | Class assignments, quizzes, examinations |
| 3.3 Distinguish the different levels of involvement used by businesses when entering global markets | Class assignments, quizzes, examinations |
| 4. Develop interpersonal and effective communication skills through appropriate interactions with peers, faculty, and guest speakers. (Goal 3.4) | |
| 4.1 Conduct presentations on business concepts | Team/individual presentations |
| 4.2 Articulate business concepts and ideas related to class interactions and discussions. | Class activities and participation |
Required Textbooks
- Foundations of Business, 7th Edition, Pride, Hughes, and Kapoor. Cengage, 2022
ISBN: 9780357717943
Other Required Materials
- Technology requirements:
- Regular and frequent access to a computer that is 0 - 5 years old, with at least 1GB of RAM
- Reliable high-speed internet access (broadband, cable, or fiber)
- An up-to-date web browser (Safari, Chrome, Internet Explorer, or Firefox)
- Microsoft Windows (Vista, 7 or later) or Mac OS X
- Able to print documents
- Able to record yourself and upload video posts/assignments
- Additional requirements as noted in course syllabus or as specified by instructor
- Access to a cloud/google drive
- Computer Lab with connections to online services and media projection equipment
- Microsoft 365
- Webcam with MP4 video capability
Computing Studies
Course Number NACT-120 Credits 3
Instructor: Jennifer Cornwell
This course is an introduction to using general-purpose software tools. The tools to be covered include word processing, spreadsheet, database, and presentation software as well as an email client. Students will do hands-on work in each application.
Goals
- To master the basic features of an integrated software package or suite that includes email, word processing, spreadsheet, database and presentation software.
- To learn how to select the right application for a task.
- To learn how to combine the features of several applications in order to perform a task.
- To develop the computer terminology and technical reading and writing skills to effectively use office applications.
Topics
- Windows Operating System
- Exploring the Basics
- Working with Files
- Microsoft Word
- Creating a Document
- Editing and Formatting a Document
- Creating a Multiple-Page Report
- Desktop Publishing a Newsletter
- Microsoft Excel
- Using Excel to Manage Financial Data
- Working with Formulas and Functions
- Developing a Professional-Looking Worksheet
- Working with Charts and Graphics
- Microsoft Access
- Introduction to Microsoft Access
- Creating and Maintaing a Database
- Querying a Database
- Creating Forms and Reports
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Creating a PowerPoint Presentation
- Appling and Modifying Text and Graphic Objects
- Integrating Word, Excel, Access and PowerPoint
Learning Outcomes
|
Outcome: |
Assessment Method |
|
Assignment and exams |
|
Assignments and exams |
|
Assignments and exams |
|
Assignments and exams |
|
Assignments and exams |
|
Assignments and exams |
|
Assignments and exams |
|
Assignments and exams |
|
Assignments and exams |
|
Assignments and exams |
Required Textbook
- Technology for Success and Illustrated Series Collection, Microsoft 365 & Office 2021, 1st Edition, Beskeen, Campbell, Ciampa, Clemens, Duffy, Freund, et al.
ISBN: 9780357675038 - Google Apps Made Easy: Learn to work in the cloud (Computers Made Easy Book 7), James Bernstein, 2019.
Other Required Materials
- Microsoft Office Suite (most recent version) is required for this course
Course Number NACT-150 Credits 3
Instructor: David Cockerham-O’Donnell
This course introduces the fundamental hardware concepts of Windows-based computers. The skills required to install, upgrade and maintain computers are presented. The course provides students with methodologies and hands-on activities related to the configuration, diagnosis, repair, upgrade, and preventive maintenance of computer hardware, input/output devices and data communications. Topics include the basic functions and use of test equipment, logical troubleshooting of internal system conflicts and faulty peripherals, and electrical safety.
Goals
- To learn how the CPU has developed and the future direction of CPU development
- To understand the functions and settings of all the components in a Windows-based PC and how they interact
- To develop the skills to be able to assemble a PC from individual components
- To learn how to install and configure a Windows operating system
- To develop the skills to be able to perform common PC upgrades
- To develop the critical thinking, logic, and technical skills needed to troubleshoot and repair PCs
- To learn how to obtain technical information on hardware and/or configurations via on-line and digital resources
- To develop the skills to be able to set up and troubleshoot peripherals
- To learn computer-related preventive maintenance, safety, and environmental issues
- To develop the reading skills needed to understand technical materials such as college textbooks, professional journals, and manuals provided by the computers manufacturer
- To develop the technical writing skills needed to document PC problems and how they were resolved
Topics
- Hardware components
- I/O Devices
- Primary Storage Devices
- External devices
- The Motherboard
- CPU and Chip Set
- Expansion Slots
- Electrical System
- Assemble a PC from components
- System Resources
- IRQ
- DMA Channels
- I/O
- Memory
- Boot up configuration
- Electricity and Power Supplies
- Basic introduction to electricity
- Preventive Maintenance & Care of PC
- Protecting your computer against electricity static discharge
- Electromagnetic interference
- Surge protection and UPS
- The System Board
- Installation / configuration
- Configure and upgrade a PC
- Supporting I/O devices
- Installing and Configuring Peripheral Devices
- Using Various Ports and Expansion Slots
- Installing Storage Devices
- Storage Devices
- Hard disks priority
- Partitions
- RAID
- Various other storage devices
- System Upgrading and Optimizing
- Motherboard, Boot up system and memory
- Processor speed and compatibility
- Power supply output capacity
- Bus types and characteristics
- Notebooks, mobile devices
- Preventive and Maintenance
- Diagnosing and Troubleshooting
- Disposing and recycling of computer component and peripherals
Learning Outcomes
| Outcome: At the completion of this course, students will be able to: |
Assessment Method |
|
Assignments and exams |
|
Lab activities and exams |
|
Lab activities and exams |
|
Lab activities and exams |
|
Lab activities and exams |
|
Lab activities and exams |
|
Lab activities, assignments, and exams |
|
Lab activities and exams |
|
Lab activities and exams |
|
Lab activities and exams |
|
Lab activities and exams |
|
Lab activities and exams |
Required Textbook
- CompTIA A+ Guide to IT Technical Support, Jean Andrews, 11th Edition. Cengage, 2022
ISBN: 9780357674161
Other Required Materials
- Computer Parts and Components
- Computer Tool Kit
Course Number NACA-172 Credits 3
Instructor: Mark Reynolds
This course introduces students to web page and small-scale website development. Through hands-on laboratory experiences, students will learn the fundamental concepts needed to construct web pages that follow appropriate coding standards as well as basic design principles to present content in an attractive and organized manner. Topics include HTML, CSS, graphical elements, website publishing, and transfer protocols.
Goals
- To understand what the Internet is, how browsers display web pages, and the history of the Internet
- To develop the skills to create a basic website using valid HTML tags, CSS, graphics and links
- To understand design principles as they relate to web page design
- To understand how to search for, use, and manipulate a variety of digital resources, and the legal implications of their use
- To learn how to use both Windows and UNIX operating environments for file management and application tasks
- To develop the study skills and the independent learning skills needed to succeed in baccalaureate level courses
- To develop the writing skills needed to present text-based information on a web page in a clear, concise and organized manner
- To develop the reading skills needed to understand technical materials such as books, journals, and manuals related to web development
Topics
- Introduction to the Internet
- Internet browsers and interoperability
- Internet addressing
- History of the WWW and Internet
- HyperText Markup Language 5 (HTML 5)
- HTML tags and styles
- Basic HTML Structure
- Basic HTML Formatting
- Images
- Locating digital resources
- Copyright and IP issues
- Image creation and manipulation
- Links
- Tables
- Multimedia
- Cascading Style Sheets 3
- Defining selectors
- Formatting with Styles
- Layout with Styles
- W3C Validation
- Search and metadata
- Accessibility
- Alt and Title attributes
- Web Content Accessibility Guidelines
- Internet Protocols
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
- Secure FTP
- Basic Web Page Design
- Content Creation/Organization
- User experience and usability
- Navigation design
- UNIX Operating System
- File and directory management
- Access permissions
Learning Outcomes
| Outcome: At the completion of this course, students will be able to: | Assessment Method |
| 1. Utilize basic Internet protocols and tools including FTP | Class exercises, Projects, Quizzes, & Tests |
| 2. Identify key figures and events in the development of the Internet and the World Wide Web | Projects, Quizzes & Tests |
| 3. Create web pages using valid HTML 5 and CSS 3 including graphics and links | Class exercises, Projects, Quizzes, & Tests |
| 4. Use graphic tools to optimize images for web pages | Class exercises, Projects, Quizzes, & Tests |
| 5. Upload pages to a web server | Class exercises, Projects, Quizzes, & Tests |
| 6. Demonstrate knowledge of graphic and information design as well as web design principles to create valid web pages | Class exercises, Projects, Quizzes, & Tests |
| 7. Demonstrate knowledge of digital imaging concepts such as file formats, resolution, color models, and compression methods | Class exercises, Projects, Quizzes, & Tests |
| 8. Perform a search to gather information from the Internet | Class exercises & Projects |
| 9. Demonstrate an understanding of the importance of copyright laws and citing digital sources | Projects |
| 10. Perform basic file and directory management tasks in the UNIX environment such as creating, deleting, and renaming items, and changing access permissions | Class exercises, Projects, Quizzes, & Tests |
| 11. Demonstrate the ability to create valid web pages without the use of external resources | Quizzes & Tests |
| 12. Research and present content on a web page in a clear, concise, and organized manger | Class exercises & Projects |
| 13. Demonstrate the ability to read web references to independently and correctly use new features of HTML | Class exercises, Projects, Quizzes, & Tests |
| 14. Use CSS 3 to support responsive web pages | Class exercises, Projects, Quizzes, & Tests |
Required Textbook
- Basics of Web Design: HTML 5 & CSS, 5th Edition, Terry Felke-Morris. Harper College, 2020
ISBN: 9780135225486
Other Required Materials
- Computers
- Keyboard and mouse
- Internet connection
- Text editor (for instance: Freeware)
- Image editor (for instance: Photoshop or Gimp)
- Server space
Course Number NACT-230 Credits 3
Instructor: Michael Berrios
This course introduces students to the fundamental concepts and terminology of computer programming. Emphasis will be placed on developing problem-solving skills in designing and writing simple computer programs. The course covers such topics as developing flowcharts, algorithms and pseudocode, and introduces students to variables, operators, conditional statements, looping statements, data structures, error-handling and debugging, and user interface design. The course assumes no programming background. (Pre-requisites: NACT-170 Introduction to Web Development, NMTH-120 or above).
Goals
- To understand programming concepts and terminology.
- To develop the critical thinking and problem solving skills needed to write well structured, syntactically correct programs that solve general application problems.
- To learn to appropriately use the components of a programming language, including variables and data types, relational and logical operators, branching, and looping, and data structures.
- To develop the skills to read, trace, and understand simple code.
- To develop the skills to write, test, and debug code to solve a simple problem.
- To successfully use many features of a programming language compiler to create, debug, and execute programs.
- To enhance students' reading and writing abilities.
Topics
- Introduction to Programming
- Overview of Computer Programming Languages
- The Software Development Process
- Software Development Life Cycle
- Algorithms
- Flowcharts
- Pseudocode
- Variables, Data, Input, and Output
- Variables
- Data Types
- Declarations
- Operators and Expressions
- Arithmetic
- Relational
- Logical
- Operator Precedence
- Decisions
- If Statements
- If-Else Statements
- Switch Statements
- Repetitions
- For Loops
- While Loops (Pretest Loops)
- Do-While Loops (Posttest Loops)
- Arrays
- Use arrays for storage and retrieval of data in a program
- Introduction to Developing a User Interface
- How to design user interface for software applications
- Best practices for user interface design
- Building a user interface.
Learning Outcomes
| Course Learning Outcome | Assessment Method |
| 1. To understand programming concepts and terminology. | |
| 1.1 Understand what software development is and what software developers do. | Assignments, Class Exercises, and Exams |
| 1.2 Describe the purposes of programming and software development. | Assignments, Class Exercises, and Exams |
| 1.3 Define an integrated development environment. | Assignments, Class Exercises, and Exams |
| 2. To develop the critical thinking and problem solving skills needed to write well-structured, syntactically correct programs that solve general application problems. | |
| 2.1 Describe the software development process, its purpose, critical steps, and where programming fits in that process. | Assignments, Class Exercises, and Exams |
| 2.2 Identify a problem that requires a programmed solution. (algorithms) | Assignments, Class Exercises, and Exams |
| 2.3 Describe problem-solving techniques. | Assignments, Class Exercises, and Exams |
| 3. To learn to appropriately use the components of a programming language, including variables and data types, relational and logical operators, branching, and looping, and data structures. | |
| 3.1 Demonstrate the use of variables. | Assignments, Practice Exercises, and Exams |
| 3.2 Describe the various data types you can use to declare variables. | Assignments, Practice Exercises, and Exams |
| 3.3 Demonstrate the use of operators including arithmetic, relational, and logical operators. | Assignments, Practice Exercises, and Exams |
| 3.4 Demonstrate the use of If, If-Else, and Switch statements. | Assignments, Practice Exercises, and Exams |
| 3.5 Demonstrate the use of For, While (Pretest), and Do-While (Posttest) Loops. | Assignments, Practice Exercises, and Exams |
| 3.6 Identify and troubleshoot syntax, runtime and logic errors. | Assignments, Practice Exercises, and Exams |
| 3.7 Create and use arrays. | Assignments, Practice Exercises, and Exams |
| 4. To develop the skills to read, trace, and understand simple code. | |
| 4.1 Trace program logic to identify logic errors and/or program output. | Assignments, Class Exercises, and Exams |
| 5. To develop the skills to write, test, and debug code to solve a simple problem | |
| 5.1 Write computer programs to solve problems using features such as input and output statements, conditional statements, looping statements, and arrays. | Assignments, Practice Exercises, and Exams |
| 5.2 Employ various techniques for testing and debugging computer programs to ensure accurate results. | Assignments, Practice Exercises, and Exams |
| 6. To successfully use many features of a programming language compiler to create, debug, and execute programs. | |
| 6.1 Define an integrated development environment. | Assignments, Class Exercises, and Exams |
| 6.2 Identify the features of a good user interface design for software applications. | Assignments, Class Exercises, and Exams |
| 6.3 Demonstrate proficiency in using the programming language in developing creative solutions to solving problems. | Assignments, Class Exercises, and Exams |
| 6.4 Illustrate how pseudocode and flowcharts are used in creating computer programs. | Assignments, Class Exercises, and Exams |
| 7. To enhance students’ reading and writing abilities. | |
| 7.1 Write clear program documentation including the purpose of the program and comments on the function of program logic. | Assignments and Class Exercises |
| 7.2 Demonstrate an understanding of programming concepts and programming design through reading. | Assignments and Class Exercises |
| 7.3 Demonstrate an understanding of programming concepts and programming design in writing. | Assignments and Class Exercises |
Required Textbook
- Starting Out with Visual C#, 6th Ed. by Tony Gaddis (ISBN 9780138087562)
Other required materials
- Computers
- Internet connection
- Microsoft Visual Studio
Engineering Studies
Course Number NPMT-101 Credits 3
Instructor: Mark Davis
Students develop the basic skills necessary to read and interpret fundamental engineering drawings of details, subassemblies and assemblies.
Goals
- Develop the skills necessary to read, analyze and interpret standard engineering drawings
- Learn to apply these skills in problem-solving situations
- Develop the skills necessary to communicate technical information with co-workers
- Develop the ability to apply math and engineering graphics skills to solve technical graphic problems
- Develop the ability to use basic shop math to perform all the calculations necessary to interpret basic engineering drawings
Topics
- Common fractions, decimal fractions and percentage
- Engineering drawing nomenclature and symbols
- Dimensioning Systems
- Single-view and detail drawings
- Sketching views from objects and isometric drawings
- Tolerances
- Arcs and circles
- Projections
- Multi-view drawings
- Angles and angular dimensions
- Machined features
- Surface roughness
- Sectional Views
- Threaded hole specifications
- Metric Drawings
- Introduction to Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing
Learning Outcomes
|
Outcome: At the completion of this course, students will be able to: |
Assessment Method |
|
Exams, Homework, Classwork |
|
Exams, Homework, Classwork |
|
Exams, Homework, Classwork |
|
Exams, Homework, Classwork |
|
Observation |
|
Exams, Homework, Classwork |
Required Textbook
- Interpreting Engineering Drawings, 8th Edition, Ted Branoff, Cecil Jensen, and Jay Helsel. Cengage, 2016
ISBN: 9781133693598
Course Number NCAD-150 Credits 3
Instructor: James Fugate
The objective of this course is to introduce students to engineering graphics as a means of communication in the technical fields of architecture, engineering and construction (A/E/C). The course is laboratory oriented and provides the student with basic skills to create professional 2D drawings with this comprehensive first course in the use of AutoCAD software for mechanical, architectural and civil drawings. The course assumes no prior knowledge of engineering drawing or CAD.
Goals
- Develop reading, writing and critical thinking skills related to engineering graphics
- Understand proper computer usage and lab safety procedures
- Learn file management techniques and understand various file formats for CAD programs
- Know how to set up CAD drawing parameters for different disciplines including mechanical, architecture and civil
- Develop basic CAD skills to create, modify and manipulate 2D technical drawings
- Understand different procedures for printing and plotting CAD drawings
- Develop basic skills in free hand lettering and technical sketching
Topics
- Introduction to Computer Aided Drafting
- Introduction to the AutoCAD interface
- Navigating the AutoCAD environment
- Understanding drawing in ‘real world’ scale and the Cartesian coordinate system
- Basic 2D object construction tools
- 2D geometric construction and editing tools
- Object properties and organization
- Basic dimensioning and notes
- Templates, layouts and plotting
- Freehand lettering and technical sketching
- Incorporating multimedia resources such as videos, sound, and scripts
- Creating and processing forms using a CGI
Learning Outcomes
|
Outcome: At the completion of this course, students will be able to: |
Assessment Method |
|
Exams, Homework |
|
Lab Exercises |
|
Exams, Homework, Lab Exercises |
|
Exams, Homework, Lab Exercises |
|
Exams, Homework, Lab Exercises |
|
Exams, Homework, Lab Exercises |
|
Exams, Homework, Lab Exercises |
|
Homework, Lab Exercises |
Required Textbook
- Introduction to AutoCAD 2020: A Modern Perspective, 1st Edition, Paul F. Richard. Pearson, 2020
ISBN: 9780135576878
Other Required Materials
- AutoCAD software is required for this course
Course Number NPMT-214 Credits 3
Instructor: Marcus Holmes
Students develop engineering skills in engineering graphics and solid modeling. Students will use computer-aided drafting (CAD) as a tool to generate 2D graphics and 3D solid models. The course is laboratory oriented and provides the student with basic skills in spatial visualization, freehand sketching, parametric solid modeling, and creation of engineering drawings which meet industrial drafting standards.
Goals
- Understand how to specify and control functional requirements through an engineering design process
- Develop the conceptual and visualization skills required to create and read engineering documentation
- Develop free hand sketching skills to communicate functional requirements of design concepts
- Create detailed engineering drawings in a standard industrial format
- Communicate engineering related solutions using engineering graphics
- Develop reading skills needed to read and understand technical materials related to computer aided drafting applications
- Develop writing skills needed to communicate technical information on the job
Topics
- Design cycle
- Freehand sketching and visualization
- Creation of 2D drawings
- 3D solid model
- Industry drafting standards
- Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T)
- Assembly construction
- Rapid Prototype
Learning Outcomes
| Outcome: At the completion of this course, students will be able to: |
Assessment Method |
| 1. Apply sketching skills of parts and assembly, concepts, and engineering Graphics | Lab Activities |
| 2. Apply visualization skills such as 2D to 3D conversion and perspective Views | Lab Activities |
| 3. Utilize basic measuring equipment and formulate GD&T specifications of a selected part | Lab Activities |
| 4. Create parts and assemblies using a 3D parametric solid modeling computer program | Lab Activities |
| 5. Generate detailed orthographic and axonometric drawings including proper dimensions, tolerance of parts and notations in a standard industrial format | Lab Activities |
| 6. Calculate size limits based on class of fit | Lab Activities |
| 7. Formulate and organize a design concept | Projects |
| 8. Demonstrate the ability to create quality solid models, engineering drawings and prototypes in a timely fashion | Projects |
| 9. Create an assembly drawing of parts | Projects & Final Exam |
| 10. Demonstrate ability to effectively make presentations | Presentations & Final Exam |
Required Textbook
- Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SOLIDWORKS 2021, 17th Edition, William Howard and Joseph Musto. McGraw Hill, 2022
ISBN: 978126072713
Other Required Materials
- Maximum of 10 computers which includes an installation of 2D/3D related software such as AutoCAD, SolidWorks and MasterCAM
Graphic Technology
We strongly encourage the following course progression: Visual Idea Development for sophomores, Page Layout for juniors, and Raster and Vector Graphics for seniors.
Course Number NGRD-115 Credits 3
Instructor: Laural Hartman
Course is open to all high school students. This course gives students the opportunity to see themselves, their experiences and their environment as sources of creativity, through a variety of activities which will include classroom discussions; videos of artists; visiting a gallery; keeping documented written and illustrated journals, sketchbooks; and working with a team to do a project. Students learn strategies for developing concepts and organization of thought processes as well as systems to formulate solutions to design problems. The library is used for development of research skills for written and visual content. Credits: 3
Goals
- Develop reading, writing, analytical thinking, and problem-solving skills related to visual idea development
- Develop the ability to see one’s experience and environment as a source of creativity
- Familiarize the student with development and organization of thought processes and systems to formulate solutions to design problems and handle abstract concepts
- Develop team and individual approaches to problem-solving and critique
Topics
- Mental Flexibility and Generating Ideas
- Communicating with Myself by Using a Journal Sketchbook
- The Design Process
- Finding Library Resources
- The Team Spirit
- Other Artists’ Creativity
- Reference Files/Sources and Copyright Laws
- Brainstorming Strategies
- Team Project
Learning Outcomes
| Outcome: At the completion of this course, students will be able to: | Assessment Method |
| 1. Use the library and other resource locations for development of research skills | Successful completion of projects; presentations; critique |
| 2. Use design periodicals/annuals for reference | Presentations; critique |
| 3. Use “swipe” (idea) files for reference | Presentations; critique |
| 4. Define copyright laws and their relation to the use of graphic images for design problem-solving | Presentations; critique |
| 5. Work successfully as part of a team to solve design problems | Successful completion of projects; presentations; critique |
| 6. Use a self-documented journal as a means of recording ideas for future design problem-solving | Successful completion of projects; presentations; critique |
| 7. Use a sketchbook as a means of recording ideas for future design-problem solving. Identify design problem-solving methods used by professional designers | Successful completion of projects; presentations; critique |
| 8. Identify design problem-solving methods used by professional designers | Successful completion of projects; presentations; critique |
| 9. Develop personal design problem-solving strategies that are drawn from the student’s own personal experiences and environmental influences | Successful completion of projects; presentations; critique |
| 10. Use basic vocabulary related to design problem-solving | Critique |
| 11. Use team and individual approaches to critique | Successful completion of projects; presentations; critique |
Other Required Materials
- Computers with word processing software
- Black marker (broad and fine nibs such as Sharpie)
- Black pen (uni-ball micro)
- Prismacolor colored markers (12 colors)
- Travel watercolor box (Sakura Koi Watercolor Field Sketch Box, 18 Color Set)
- White-out pens
- 12" ruler
- HB pencil
- Eraser
- Sharpener
- Sketchbook (5 x 8") OR (9 x 12”) (Strathmore Visual Journal Drawing)
- Scanner (to scan and upload all sketches) and/or digital camera
- Other art materials for the team project in addition to $10 cash per team member for the art materials for the team project
Recommended books
- Journal Sparks by Emily Neuburger
- The Sketchbook Idea Generator by Jennifer Orkin Lewis
- Biomimicry: Inventions inspired by Nature by Dora Lee
Course Number NAIS-130 Credits 3
Instructor: Ernie Roszkowski
This course is open to seniors and introduces students to the skills needed for the successful production and manipulation of raster and vector images using image creation and production software. Students will work in bitmap and vector applications, producing and editing with the tools and techniques offered by the software programs such as selection techniques, basic layer controls, digital masking, image correction and enhancement. Additional topics will include the relevance of image size, resolution and file format specifications when working with raster and vector images. Comprehension and correct usage of terminology and concepts are emphasized.
Goals
- Develop reading, writing, analytical thinking, and problem solving skills related to
bitmap and vector images and basic digital image manipulation. - Learn how to use raster and vector programs to create and manipulate images.
- Foster ability to make fundamental image manipulation decisions.
- Understand how to design and evaluate digital images.
- Enhance knowledge needed for saving and managing graphic files in various file
formats for screen, digital printer, or press output. - Understand how to compress, store and retrieve digital images.
- Learn to make appropriate decisions regarding file formats and file management.
- Prepare for the job application and interview, resume writing, and portfolio building processes.
Topics
- Definition, purpose, benefits, differences, between bitmap and vector graphics
- Basic tools, menus and controls needed for bitmap and image creation and editing
- Working with selections
- Layers in bitmap graphics
- Correcting and enhancing digital photos
- Masks and channels
- Type
- Vector tools in a bitmap application
- Selecting and aligning tools
- Creating shapes combining and editing
- Transforming objects
- Drawing with vector tools
- Color
- Working with type
- Working with Layers in vector graphics
- Working with perspective drawing
- Blending and adjusting color and shapes
- Working with Brushes
- Applying and editing effects
- Appearance attributes and graphic styles
- Vector graphics and other applications
Learning Outcomes
|
Outcome: At the completion of this course, students will be able to: |
Assessment Method |
|
Successful completion of projects per specified criteria; tests and exams |
|
Successful completion of projects per specified criteria; tests and exams |
|
Successful completion of projects per specified criteria; tests and exams |
|
Successful completion of projects per specified criteria; tests and exams |
|
Critiques, class discussions, tests and exams. |
|
Successful completion of projects per specified criteria; tests and exams |
|
Successful completion of projects per specified criteria; tests and exams |
Required Textbooks
- Adobe Illustrator Classroom in a Book (2024 release) by Brian Wood (ISBN 138263825)
- Adobe Photoshop Classroom in a Book (2024 release) by Conrad Chavez (ISBN 138262527)
Other Required Materials
- Adobe Photoshop and Illustrator (most recent versions) are required for this course
Course Number NAIS-150 Credits 3
Instructor: Andrea Zuchegno
Course is open to juniors and above. Students will use page layout (desktop publishing) applications to design and produce pages and documents to given specifications. Skill development will include importing and placing text and graphic files, the application of style sheets, templates, snippets, libraries, and color specifications. The application of design and typographic principles, industry terminology, measurement systems, font management, and file management are also covered.
Goals
- Develop reading, writing, analytical thinking, and problem solving related to desktop publishing.
- Improve technical skills in using software applications to manipulate and efficiently utilize the elements of a document, including typography, design, graphics and layout.
- Prepare for a job application and interview, including resume writing and portfolio building processes.
Topics
1.0 Job Specifications
1.1 Measurement
1.2 Fonts
2.0 Graphics
2.1 Bitmapped vs. vector files and formats
2.2 Element creation (rules, tints, etc.)
2.3 Image manipulation
3.0 Electronic Page Layout
3.1 File setup
3.2 File naming and identification
3.3 Document layout
3.3.1 Pagination
3.3.2 Master pages
3.3.3 Templates
3.3.4 Libraries
3.3.5 Tables
3.4 Placing text
3.4.1 Text flow
3.4.2 Style sheets
3.5 Placing graphics
3.5.1 Graphic manipulation
3.5.2 Linking
3.6 Integrating text and graphics
3.7 Color: Color systems and techniques
3.8 File saving
3.9 Use of Help menu, on-line help, and documentation
4.0 Document Output
5.0 File Management
6.0 Design Fundamentals
6.1 Design principles: balance, emphasis, rhythm, unity, figure/ground
6.2 Design elements: line, shape, value, color, texture, type
6.3 Formats and grids
Learning Outcomes
|
Outcome: |
Assessment Method |
|
Projects and performance tests |
|
Projects and performance tests |
|
Projects and performance tests |
|
Written and performance tests |
|
Written and performance tests |
|
Projects and performance tests |
|
Projects and performance tests |
|
Written and Performance tests |
Required Textbook
- Adobe InDesign Classroom in a Book (2024 release) by Kelly Anton and Tina DeJarld (ISBN 138263914)
Other Required Materials
- Adobe InDesign (most recent version) is required for this course
Course Number N3DG-110 Credits 3
Instructor: Philip Pham
This course is an introduction to the representation of form in three-dimensional space using 3D software. The course focuses on the development of visual and verbal vocabulary as a means of exploring, developing, and understanding 3D modeling techniques. Topics include the basics of lines, planes, contour, transforming lines into forms, interaction of lights and surfaces, perspective, resolution of geometry, and rendering. Projects will include modeling organic and inorganic forms, composition and level of detail. Structured assignments develop skills in concept generation, basic form making, techniques and craftsmanship. Emphasis is placed on workflow, teamwork, and the technical and aesthetic aspects of each project.
Goals
- Develop reading, writing, analytical thinking, and problem-solving skills related to 3D
- Develop a solid foundation in visual elements and principles of design related to 3D
- Learn and understand the process of workflow and research
- Learn and develop skills to create 3D models using 3D software
- Learn modeling techniques
- Understand concepts related to basic surfaces and lighting
- Learn about basic composition in 3D space
- Learn and understand rendering methodologies
- Learn about file references
- Develop team and individual approaches for problem solving and critiquing
- Prepare projects for inclusion in the portfolio
Topics
- Visual and verbal vocabulary of design in 3D graphics
- Basic information about three-dimensional space
- Overview of visual elements and principles of three-dimensional modeling
- Research and Project Planning for 3D modeling
- Introduction of 3D software
- Types of models to create organic/inorganic forms
- Polygons
- NURBS
- Subdivisions
- Introduction to basic material types
- Introduction to basic lightings
- Introduction to basic rendering techniques with its basic components
- Introduction to file references within 3D software
- Introduction to demo-reel
Learning Outcomes
| Outcome: At the completion of this course, students will be able to: | Assessment Method |
| 1. Distinguish the visual elements and principles of design related to 3D | Successful completion of written assignments or quizzes. |
| 2. Demonstrate an understanding of the process of workflow and how to research to create and develop 3D models | Successful completion of written assignments or quizzes. |
| 3. Apply 3D techniques using Polygons, NURBS, and Subdivisions using 3D software | Successful completion of projects. |
| 4. Recognize the different types of lighting and basic Surface and apply on 3D models | Successful completion of projects. |
| 5. Develop and design basic composition using 3D software | Successful completion of projects. |
| 6. Identify and compute the rendering settings to render final images | Successful completion of projects. |
| 7. Generalize and examine the industry’s standard file structures and references using 3D software | Successful completion of written assignments. |
| 8. Work as part of a team to solve design problems and to accept and offer feedback | Successful demonstration of team problem solving and critique methods per specified criteria. |
Other Required Materials
- Autodesk Maya 2024 Basics Guide by Kelly L. Murdock (ISBN 978-1630575809)
Liberal Studies
Course Number UWRT-100 Credits 3
Instructor: Cindy Officer
Critical Reading and Writing is a one semester, three-credit course limited to 15 students per section. This course is designed to help students develop the literacy practices they will need to be successful in their First-Year Writing course. Students will read, understand, interpret, and synthesize a variety of texts. Assignments are designed to challenge students intellectually, culturally and rhetorically. Through inquiry-based assignment sequences, students will improve their writing by developing academic research and literacy practices that will be further strengthened in First-Year Writing. Particular attention will be given to critical reading, academic writing conventions, and revision. Small class size promotes frequent student-instructor and student-student interaction. The course also emphasizes the principles of intellectual property and academic honesty in academic writing.
Goals
- Students develop the academic literacy practices (including critical reading, academic writing, and research) required for successful engagement with and completion of the research and writing tasks assigned in First-Year Writing.
- Students develop critical reading practices to recognize and respond to purpose, audience, and stance.
- Students use digital and print resources for research, to begin to recognize the differences as well as the connections among facts, opinions, and values presented in a variety of sources.
- Students synthesize information from a variety of readings, selecting evidence to incorporate into writing assignments, and organize and manage source information.
- Students compose, revise, and edit written assignments following conventions of organizing, developing and supporting a claim based on course readings.
- Students understand the principles of intellectual property and academic honesty for academic writing and learn to use citation formats.
Topics
- Critical reading and thinking (e.g., summarizing, paraphrasing, incorporating, responding, and reflecting);
- Information literacy (i.e., finding, evaluating, and integrating information from print and digital resources);
- Writing processes (i.e., prewriting, drafting, revising, editing, and using feedback from peers and instructor); and
- Clear expression of ideas (e.g., writing coherent sentences and paragraphs, revising for style and clarity).
Learning Outcomes
| Outcome: At the completion of this course, students will be able to: |
Assessment Method |
|
The instructor will assign and assess classroom and written discussion of at least 5 complex readings that include inference, evidence, and claims. The instructor will assign low stakes writing weekly to assess student progress in selecting a focus, and organizing and managing information. |
|
The instructor will assign and assess classroom and written discussion of at least 5 complex readings that include inference, evidence, and claims. |
|
The instructor will assign low stakes writing weekly to assess student progress in selecting a focus, and organizing and managing information. |
|
The instructor will assign low stakes writing weekly to assess student progress in selecting a focus, and organizing and managing information. |
|
The instructor will assess student success in achieving writing outcomes by means of scaffolded assignments that include multiple drafts of 3 major written assignments. |
|
The instructor will assess student success in achieving writing outcomes by means of scaffolded assignments that include multiple drafts of 3 major written assignments. |
|
Additionally, all students will meet individually with the instructor for progress conferences at least twice during the semester to talk about their reading and writing. |
Other Required Materials:
- Everyone’s an Author, 4th Ed. by Andrea Lundsford, et al. (ISBN 1324045108)
- Other resources, such as academic databases, readings, technology support needs, etc.
Course Number LEAD-101 Credits 3
Instructor: Denise Kavin
This course is designed to provide a basic introduction to inclusive leadership and community development by focusing on what it means to be a good leader who facilitates community development. Emphasis in the course is on the practice of leadership. The course will examine topics such as: understanding leadership, recognizing leadership traits, engaging people’s strengths, understanding philosophy and styles, attending to tasks and relationships, developing community leadership skills, creating a vision, establishing a constructive community climate, listening to out-group members, handling conflict, addressing ethics in community leadership, overcoming obstacles, and ensuring inclusion of racial and disability justice frameworks in various community leadership approaches. Students will assess their leadership traits and skills to improve their own leadership performance.
Goals
- Students will gain knowledge of inclusive leadership theories to identify and implement strategies to achieve community goals.
- Gain knowledge of research methodologies in preparation for community–based leadership roles.
- Demonstrate effective written and oral communication abilities.
Topics
- 1. Leadership
- 1.1 Understanding Leadership for community
- 1.2 Defining Leadership
- 1.3 Global Leadership Attributes
- 1.4 Practicing Leadership
- 1.5 Recognizing Your Traits
- 1.6 Historical Leaders
- 1.7 Leadership Studies
- 1.8 Strength-based leadership
- 1.9 Ethics of leadership
- 2. Leadership Styles
- 2.1 Leadership Styles
- 2.2 Tasks and Relationships
- 2.3 Developing Leadership Skills
- 3. Vision
- 3.1 Creating a vision for community
- 3.2 Characteristics of a vision
- 3.3 Vision articulation
- 3.4 Vision implementation within the community
- 3.5 Vision for different contexts
- 4. Constructive Community Climate
- 1 Understand the concept of constructive climate
- 2 Explain the process for providing constructive feedback
- 5. Conflict
- 5.1 Kinds of Conflict
- 5.2 Approach to Conflict
- 5.3 Strategies for Conflict Resolutions
- 5.4 Styles of Approaching Conflict
- 5.5 Handling Conflict
- 5.6 Communication and Conflict
- 6. Accessibility and intersectionality in leadership
- 6.1 Fundamentals of disability and racial justice
- 6.2 Strategies for inclusion and access in leadership
Learning Outcomes
|
Outcome: |
Assessment Method |
|
Written paper |
|
Written paper |
|
Written paper |
|
Written paper |
|
Written paper and final project |
|
Written self-assessment |
Possible Resources:
- Leadership: Theory and Practice 5th Ed. by Northouse, P.G. (ISBN1506362311)
Mathematics
Course Number NMTH-140 Credits 3
Instructor: Stowe Beecher
This project-based course is intended for students interested in the exploration of mathematical thinking and procedures. It includes applications to real world situations and uses problem solving skills. Topics include number sense, consumer mathematics, introduction to statistics, basic geometry, number representation, and units of measurement including conversion in English and metric systems.
Goals
- To provide and enhance a foundation in mathematical thinking and problem solving
- To explore the interface between language (English and ASL), mathematics and symbol systems
- To actively explore appropriate use of current technology in conjunction with concepts developed in the course
- To develop reading, writing and critical thinking skills related to concepts of mathematics/statistics content
- To apply and practice math skills that will be vital to success in other courses and which are important in the areas of business and the social sciences
Topics
- Number Sense
- Applications of Mental Arithmetic
- Applications of Estimation
- Review Exponents
- Relational Operations
- Scientific Notation
- Consumer Mathematics
- Review of Percents, Decimals, and Fractions
- Solving Percent Problems
- Applications
- Sales Tax, Sales Price, Income Tax
- Installment Loans
- Annuities
- Simple and Compound Interest
- Review Percent of Increase and Decrease
- Introduction to Statistics
- Population vs. Sampling
- Graphical Presentation of Qualitative and Quantitative Data
- Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median, and Mode
- Concept of Measures of Dispersion: Range, Standard Deviation
- Concept of Normal Distribution
- Scatterplot and its Correlation
- Concept of a Best-Fit Line
- Units of Measurement & Conversion in the English and Metric Systems
- Length
- Area
- Volume and Capacity
- Weight and Mass
- Temperature in Fahrenheit and Celsius Scales
- Pixel Dimension, Resolution & Image Aspect Ratio
- Geometry
- Perimeter & Circumference
- Area
- Volume
- Number Representation
- Early and Modern Numeration Systems
- Simple Grouping Systems: Egyptian
- Multiplicative Grouping Systems: Chinese
- Positional Systems: Hindu-Arabic & Roman
- Base Number Systems
- Base 10
- Binary System (Base 2)
- Octal System (Base 3)
- Hexadecimal System (Base 16)
- Base Conversion
- Operations in Base Number Systems
- Early and Modern Numeration Systems
- Supplemental Project Activities
- Strategies for Learning Mathematics
- Getting Extra Help
- Reading and Using On-Line Materials
- Writing Mathematically
- Preparing for Project Management
- Working and Communicating with other Students
- Summarizing Learning Outcomes
- Use of Calculator & Spreadsheet
- Technical Signs and Mathematics Vocabulary
- ASL Signs used in Mathematics
- How the Mathematical Concepts Relate to the Signs
- Strategies for Learning Mathematics
Learning Outcomes
| Outcome: At the completion of this course, students will be able to: |
Assessment Method |
| 1. Demonstrate the use of mental arithmetic and estimation | Project & Test |
| 2. Convert very small/large number into scientific notation and vice versa | Project & Test |
| 3. Solve written problems involving percent of increase or decrease, expressing the answer in written English | Project & Test |
| 4. Solve applied problems involving sales tax, discounts and income tax | Project & Test |
| 5. Compute simple/compound interest and future value | Project & Test |
| 6. Determine the value of an annuity and regular payments needed to achieve financial goal | Project |
| 7. Compute the periodic payment needed to meet a goal, for example: a mortgage/purchasing a new car | Project |
| 8. Find the interest, the balance due, and the minimum monthly payment for the credit card loans | Project & Test |
| 9. Describe the difference between a population and a sample | Project & Test |
| 10. Organize and present data visually | Project & Spreadsheet |
| 11. Determine and interpret the mean, median, mode for a data set | Project & Spreadsheet |
| 12. Determine and interpret the range and standard deviation for a data set | Project & Spreadsheet |
| 13. Recognize characteristics of normal distribution and understand the 68-95-99.7 rule | Project & Test |
| 14. Make a scatter plot for a table of data items, draw a best-fit line and interpret information given on the scatter plot | Project & Spreadsheet |
| 15. Convert measurements of length in the English/metric system | Project |
| 16. Convert between English and metric units of length | Project |
| 17. Convert units of area/volume | Project |
| 18. Convert weights in the English/metric system | Project |
| 19. Convert weights in the English/metric system | Project |
| 20. Convert weights between English and metric units | Project |
| 21. Convert temperatures between the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales | Project |
| 22. Solve applied problems involving pixel dimension, resolution and image aspect ratio | Project |
| 23. Calculate perimeters and areas of plane regions and solve applied problems | Project & Test |
| 24. Use formulas to calculate a circle’s circumference and area | Project & Test |
| 25. Compute the volumes of three-dimensional figures and solve applied problems | Project & Test |
| 26. Convert between base 10 and other bases | Project |
| 27. Convert between binary, octal, and hexadecimal | Project |
| 28. Add, subtract, multiply and divide in bases other than ten | Project & Test |
| 29. Work with numbers in the Egyptian, Roman & Chinese systems | Project |
Other Course Requirements
- Course should be offered in a room with a SmartBoard and related software, and dual projectors when possible because of the extensive use of technology
Performing Arts
Course Number PRFN-100 Credits 3
Instructor: Erin Auble
This course will examine the characteristics and elements of theatre and the performing arts, emphasizing the principles and conventions that guided theatre productions through history. The course examines the ways that theatre influences and is influenced by cultures and by individual life experience. Particular attention is paid to the development of scripts, visual theatre, theatre vocabulary, and the emergence of Deaf and multicultural theatre. Credits: 3
Goals
- Identify characteristics and elements of drama
- Identify areas of performance in everyday activities and rituals
- Identify key figures in Deaf performance
- Distinguish among different stage forms, roles, and responsibilities
- Demonstrate reading, writing and critical thinking skills related to performing arts analysis and critique
Topics
- Script Analysis and Dramatic Literature:
- Characteristics of drama;
- Elements of drama;
- Types of composition/Genres;
- Plot and the Aristotelian system;
- Episode/Unit of action;
- Conflict Character development;
- Identification and motivation;
- Drama and the audience, immediate and after effect;
- The role of theatre in the Deaf community.
- Deaf actors and dancers;
- Performance:
- Purpose and method in acting;
- Purpose and method in dance;
- The performer’s dual nature;
- Analyzing a role;
- Systems of acting, preparation;
- Movement systems;
- Pantomime, Sign mime and translation.
- Staging
- Organizing the theatre space;
- Origins of stage design;
- Proscenium theatre/ Arena/ Thrust;
- Aesthetics and Appropriateness;
- Role of the set designer/technical director;
- Technical demands of the script;
- Role of the lighting director;
- Lighting and stage action/Lighting for ASL;
- Style, mood, and uses of color in lighting;
- Role of the costume designer;
- Costumes research;
- Physical mobility and signing in costume.
- Directing
- Functions and role of the director;
- Directional style and philosophy;
- Deaf directors;
- Relationship to the script/play creator;
- Relationship to the actors;
- Relationship to the designers;
- Relationship to the audience;
- Rehearsals; Performances.
Learning Outcomes
| Outcome: At the completion of this course, students will be able to: |
Assessment Method |
| 1. Identify characteristics of drama | Discussion, exams |
| 2. Identify the elements of drama | Discussions, exams, written critiques |
| 3. Distinguish kinds of dramatic compositions | Discussion, critique |
| 4. Trace the history of theatre to its early origins | Exams, discussion |
| 5. Trace human connections to theatre in other activities and rituals | Research project |
| 6. Identify areas of performance in everyday life | Biographical research |
| 7. Identify key figures in Deaf community theatre | Discussion, exam |
| 8. Distinguish among different stage forms | Drawing, exams |
| 9. Define the role of the set, lighting, costume designer | Discussion, exams |
| 10. Define the roles and responsibilities of the director | Tests and demonstration |
| 11. Describe various production styles and philosophies | Discussion, exams |
| 12. Identify some current trends in the performing arts | Discussion, exams |
| 13. Demonstrate reading, writing and critical thinking skills | Text analysis, written critiques |
Other Course Requirements
- Course should be offered in a room with a projector or smartboard as many of the class resources are video related.
Course Number PRFN-102 Credits 3
Instructor: instructor assignment is pending
This course introduces students to the technical and design processes of theatre, including scenery, costume, lighting, make-up, and prop craft. Students experience the range of skills needed to create successful productions, and identify their own areas of interest and strength for future theatre participation. Credits: 3
Goals
- Use, identify, and define basic stage vocabulary terms.
- Demonstrate learned technical theatre skills
- Read and analyze a text for the purposes of identifying technical theatre demands.
- Demonstrate time management.
- Identify and apply theatre practice to an area of strength or interest within stagecraft.
- Demonstrate reading, writing and critical thinking skills related to stagecraft.
Topics
- Definition of stagecraft and technical theatre
- Basic theatre personnel structure – jobs, responsibilities and opportunities
- Role of the Costume/Makeup Designer and related staff
- Costume Studio tools, equipment and set-up (sewing machines, dress forms, etc.)
- Basic sewing or craft skills
- Role of Scenic Designer, Technical Director and related staff and shops
- Basic Scenic construction skills and related safety concerns
- Properties (“props”)
- Role of Lighting Designer and related staff and shops
- Basic Lighting “hang and focus” skills
- Exploration of stage makeup
- Other aspects of stagecraft current to a production or script (puppetry, flying, scene painting)
- Discussion and understanding of a play script from a technical perspective.
Learning Outcomes
| Course student learning outcome | Assessment Method |
| Use, identify, and define basic stage vocabulary terms. | Written Exam |
| Demonstrate learned technical theatre skills | Costumes, Lighting, and Scenic Projects |
| Read and analyze a text for the purposes of identifying technical theatre demands. | Collaborative cumulative project on needs assessment |
| Demonstrate time management. | Weekly take home assignments |
| Identify and apply theatre practice to an area of strength or interest within stagecraft. | Final Project and self-assessment |
| Demonstrate reading, writing and critical thinking skills related to stagecraft. | Written exam, needs assessment, final project and self-assessment |
Other Course Requirements
- This course will benefit from a space where students will be able to work with basic power tools, hand tools, paint, stage makeup, and basic lighting equipment.
Science
Course Number NSCI-153 Credits 3
Instructor: Matt Stefano
This course covers introductory science processes using content of environmental studies as a vehicle to establish an appreciation of the scientific method, critical thinking and problem solving. The basic processes of observing, collecting data, classifying, comparing, analyzing and forming hypotheses will be addressed using the concepts of environmental studies.
Goals
- To develop reading, writing and analytical skills related to the environmental studies content and to use those skills to develop and revise written laboratory reports
- To enhance skills in communicating scientific ideas and processes in writing and face-to-face, using English and ASL
- To develop students’ ability to think critically and solve problems as they relate scientific concepts to real world issues
- To develop skills in observation, basic measurement techniques, data collection, and graphical and analytical interpretation of data
Topics
- Air Pollution
- Vehicle Pollution
- Fuel Economy
- Alternative Energy Sources
- Toxic Release Inventory
- Water Pollution
- Water Quality Monitoring
- Water Quality Testing (chemical based)
- Water Quality Testing (species based)
- Great Lakes
- Environmental Policy
- Global Warming
- Environmental Disasters
- Biodiversity
- Human Population
- Overfishing
- Technical signs and science vocabulary
- ASL signs used in this course
- How the science concepts relate to the signs
Learning Outcomes
|
Outcome: |
Assessment Method |
|
1. Research and analyze which car is the best through MPG and how high and low MPG impacts the environment |
Lab report |
|
2. Research and present various alternative energy sources by showing the pros and cons of the energy source |
Presentation, Test |
|
3. Identify trouble areas using Toxic Release Inventory reports |
Lab report |
|
4. Use technology to collect water samples to analyze and report findings |
Lab report |
|
5. Research and share environmental issues regarding the Great Lakes. |
Presentation, Test |
|
6. Discuss the importance of Biodiversity |
Homework, Test |
|
7. Analyze the impact of human population growth on the environment. |
Homework, Test |
|
8. Measure the impact of wind on air pollution |
Lab report |
|
9. Measure the impact of cars on air pollution. |
Lab report |
|
10. Measure the impact of overfishing on ecosystem and demonstrate knowledge how to reduce overfishing |
Homework, Lab report, Test |
|
11. Demonstrate cooperative problem solving with peers |
Lab activities |
|
12. Research multiple environmental disasters and demonstrate how the ecosystem was impacted |
Presentation |
Other Course Requirements
- Properly organized, equipped, and maintained science lab and access to computers
- Water Quality Testing Equipment (pH, temperature, turbidity, dissolved oxygen). Other tests can be included
- Access to water (lake, stream, river, pond, creek, etc.)
- Access to PC computers (required for software to work on)
- Access to Microsoft Office or Google
- Optional: https://www.enviroscapes.com/category/hands-on-models
Course Number NSCI-155 Credits 3
Instructor: Sarah Sarchet
This course covers introductory science processes using biology content as a vehicle to establish an appreciation of the scientific method, critical thinking and problem solving. The basic processes of observing, collecting data, classifying, comparing, analyzing and forming hypotheses will be addressed using selected concepts in biology.
Goals
- To develop reading, writing and analytical skills related to selected concepts in biology and to use those skills to develop and revise written laboratory reports
- To enhance skills in communicating scientific ideas and processes in writing and face-to-face, using English and ASL
- To develop students’ ability to think critically and solve problems as they relate scientific concepts to their health and development
- To develop skills in observation, basic measurement techniques, data collection, and graphical and analytical interpretation of data
Topics
- The Scientific Method and Hypotheses
- Homeostasis in the human body
- Circulatory System
- Respiratory System
- Excretory System
- Human Nutrition
- Macromolecules
- Digestive System
- Human Development
- Cells
- Mitosis and Meiosis
- Reproductive System
- Human Inheritance
- Genetics
- Biotechnology
- Human Disease
- Bacteria & Viruses
- Circulatory System Diseases
- Respiratory System Diseases
- Excretory System Diseases
- Digestive System Diseases
- Reproductive System Diseases
- Cancer
- Technical signs and science vocabulary
- ASL signs used in this course
- How the science concepts relate to the signs
Learning Outcomes
| Outcome: At the completion of this course, students will be able to: |
Assessment Method |
| 1. Apply the process of the scientific method to formulate a hypothesis | Lab work & Laboratory Reports |
| 2. Provide examples of homeostasis within the human body | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 3. Describe the function of the following body systems: circulatory, respiratory, excretory, digestive, reproductive | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 4. Describe the structure of the heart and blood flow through it using correct anatomical terminology | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 5. Identify the flow of deoxygenated and oxygenated blood through the pulmonary and systemic circuits | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 6. Compare the structure and function of the three types of blood vessels | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 7. Discuss the dangers of high blood pressure and artery damage | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 8. Explore the role of lifestyle in cardiovascular disease | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 9. Identify and describe the major components of blood and their function | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 10. Differentiate between different blood types and explain the requirements for blood donors and recipients | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 11. Calculate max heart rate and target heart rate for a given age | Lab work & Laboratory Reports |
| 12. Identify the structures of the upper and lower respiratory tracts and their functions | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 13. Discuss how gas is exchanged through the alveoli | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 14. Describe the main disorders of the lower and the upper respiratory tracts | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 15. Explain how the nephrons of the kidney filter the blood | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 16. Discuss common excretory system disorders | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 17. Classify chemical structures of various biological macromolecules | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 18. Explain the structures, processes and functions of the organs in the digestive system | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 19. Differentiate between type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes and explain how the condition arises | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 20. Explain the following nutrition disorders: obesity, bulimia nervosa, anorexia nervosa, malnutrition | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 21. Identify organelles when presented a picture of a cell | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 22. Explain the function of cellular organelles | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 23. Identify and draw various tissue types from prepared slides | Lab work & Laboratory Reports |
| 24. Differentiate between the processes of mitosis and meiosis | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 25. Discuss common reproductive diseases and disorders | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 26. Perform analyses of Punnett squares and stated predicted ratios of phenotypes and genotypes | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
| 27. Perform DNA gel electrophoresis | Lab work & Laboratory Reports |
| 28. Read plasmid maps and predict DNA fragment sizes | Lab work & Laboratory Reports |
| 29. Graph data collected from antibiotic sensitivity testing | Lab work & Laboratory Reports |
| 30. Explain the process of invasive cancer | Assignments, Quizzes, & Exams |
Required Textbook
- Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, 6th Edition, Eric Simon, Jean Dickey, and Jane Reece. Pearson, 2019
ISBN: 9780134763453
Other Course Requirements
- Properly organized, equipped, and maintained science lab and access to computers
- Lab coats or aprons, goggles, gloves
- Electrophoresis equipment for testing DNA samples
- Lung model
- Blood pressure cuff
- Prepared slides of cells (histology)
- Urinalysis kit (Ward’s)
- Materials for dissections (kidneys, hearts, fetal pigs; dissection tray, dissection tools)
- Stopwatches/timers
- Petri dishes, TSA agar, antibiotic disc
Course Number NSCI-156 Credits 3
Instructor: Camille Ouellette
This course covers introductory science processes using the content of forensics as a vehicle to establish an appreciation of the scientific method, critical thinking and problem solving. The basic processes of observing, collecting data, classifying, comparing, analyzing and forming hypotheses will be addressed using the concepts of forensics.
Goals
- To develop reading, writing and analytical skills related to the forensics content and to use those skills to develop and revise written laboratory reports
- To enhance skills in communicating scientific ideas and processes in writing and face-to-face, using English and ASL
- To develop students’ ability to think critically and solve problems as they relate scientific concepts to real world issues
- To develop skills in observation, basic measurement techniques, data collection, and graphical and analytical interpretation of data
Topics
- Forensic Concepts and Terms
- Prediction and Hypothesis
- Documenting a Crime Scene
- Crime Scene Analysis
- Using actual data
- Using news articles
- Laboratory Techniques
- Blood
- Hair
- Fingerprints
- DNA
- Urine Analysis
- Writing a Formal Laboratory Report
- Technical signs and science vocabulary
- ASL signs used in this course
- How the science concepts relate to the signs
Learning Outcomes
| Outcome: At the completion of this course, students will be able to: |
Assessment Method |
|---|---|
|
Quizzes, Homework & Labs |
|
Quizzes, Homework & Labs |
|
Quizzes, Homework & Labs |
|
Laboratory Reports |
|
Quizzes, Homework & |
|
Laboratory Report |
|
Quizzes, Homework & Labs |
|
Lab work |
|
Quizzes, Homework & Labs |
|
Lab work |
|
Quizzes, Homework & Labs |
|
Lab work |
|
Quizzes, Homework & Labs |
|
Lab work |
|
Quizzes, Homework & Labs |
|
Lab work |
Other Course Requirements
- Properly organized, equipped, and maintained science lab and access to computers
- Electrophoresis equipment for testing DNA samples
- Micropipettes and tips
- P20
- P200
- P1000 (optional)
- Ink pads
- Regular #2 pencils
- Rulers with inches on one side and centimeters on the other side
- Bags of M&Ms, Skittles, or other differently colored candies
- Clear cups or beakers
- Masking tape
- Artificial blood
- Hair samples
- Various props such as wine glass, murder “weapons”, eyeglasses, etc.
- Scotch tape
- Compound microscopes
- Microscope slides
- Cover slips
- Clear nail polish
- Eyedroppers
- Fur samples from a dog
- Ward’s Simulated ABO & Rh Blood Typing Lab Activity (Item #470213-350, $54.79)
- Test tube racks
- Test tubes
- Negative control – distilled water
- Positive control – 0.1M sodium acetate or similar solution with pH 8-10
- Experimental blood sample – 0.1M sodium acetate or similar solution with pH 8-10 with red food cloring
- Power supply
- Combs
- Trays
- Microwave
- Bio-Rad Forensic DNA Fingerprinting Kit (Item #1660007EDU, $167.50)
- Plastic bathroom size cups
- Laundry detergent
- Contact lens solution
- Iodized salt
- 70% isopropyl alcohol
- Wood coffee stirrers or toothpicks
- Meter sticks
- Protractors
- Mortar and pestle
- Aspirin, acetaminophen (Tylenol), caffeine, pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) tablets
- Chromatography or filter paper
- Chambers for chromatography
Course Number NSCI-283 Credits 3
Instructor: Denise Lengyel
Introduces basic human development and maturation from a multidisciplinary perspective. In this course, the fields of human anatomy and physiology are merged with developmental psychology for the purpose of examining the human life cycle from a holistic perspective. Changes that take place in the structure and function of the human body are studied over nine stages of the human life span. Concurrently, psychological and cognitive development are discussed, beginning with conception and ending with death processes. Credits: 3
Goals
- To reduce negative perceptions of science and science topics
- To demystify science; i.e., the perception that science should be the exclusive concern of “experts”
- To reinforce a citizen's life-long responsibility to pay attention to scientific issues and to give students permission to form an opinion with respect to social implications of scientific developments
- To model processes and introduce tools of scientific inquiry
- To understand information in scientific literature drawn from multiple sources
- To guide students in scientific topic research
- To develop knowledge and critical thinking skills that apply to an understanding of the scientific principles supporting human development and human anatomy and physiology
- To develop knowledge of science vocabulary and utilize this vocabulary to accurately communicate current scientific phenomena
- To enhance skills in communicating scientific ideas and processes in written lab reports and face-to-face using English and ASL
Topics
- Erikson's Stages of Development
- Body Systems, Homeostasis & Disease
- Human Reproductive Anatomy, Physiology & Embryology
- Skeletal System
- Muscular System
- Integumentary System
- Nervous System & Senses
- Endocrine System
- Cardiovascular System & Blood
- Lymphatic System & Immunity
- Respiratory System
- Digestive System, Metabolism & Nutrition
- Urinary System
- Communication and Science
- Technical signs and science vocabulary
- signs used in science
- How science concepts relate to science signs
- Writing Lab Reports
- Required parts of a science lab report
- Reading and following directions
- Gathering data and communicating with lab partners
- Presenting data, results and writing conclusions
- Rewriting and improving lab report drafts
Learning Outcomes
| Outcome: At the completion of this course, students will be able to: |
Assessment Method |
| 7.1 Name eight stages of human development (Erikson's) and identify Erikson's labels for the challenges at each stage - demonstrated through written description and identification (3.3, 3.7, 3.8, 3.9) | Quizzes, Homework & Labs |
| 7.2 Identify body systems labeling anatomical models & illustrations, and through written descriptions (3.2, 3.8, 3.9) | Quizzes, Homework & Labs |
| 7.3 Identify reproductive anatomical structures for men and women, describe the physiology of gamete formation, fertilization, and embryological development - demonstrated by written descriptions (3.1, 3.3, 3.6, 3.7, 3.8, 3.9) | Quizzes, Homework & Labs |
| 7.4 For each of the systems listed above (6.4 - 6.13), identify key anatomical structures (listed in learning objectives), describe the function of each structure - demonstrated by accurately labeling anatomical models & illustrations and through written description (3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.6, 3.7, 3.8, 3.9) | Quizzes, Homework & Labs |
| 7.5 Dissect a fetal pig, identify the organs and organ systems (listed in learning objectives), and compare the anatomy of the fetus to the adult – demonstrated by written description (3.4, 3.8, 3.9) | Homework & Labs |
| 7.6 Complete dissections of selected organs (heart, brain, ovary, testis, kidney, eye, stomach, pancreas) and relate the anatomical characteristics to the physiological function of the organ as demonstrated by written descriptions (3.4, 3.8, 3.9) | Homework & Labs |
| 7.7 Research one assigned endocrine hormone and present findings to peers - demonstrated by a successfully mediated presentation, including identifying appropriate references (3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.5, 3.6, 3.8, 3.9) | Homework & Labs |
| 7.8 Express themselves effectively in common college-level written forms using standard American English | Lab Reports |
| 7.9 Review, assess, and draw conclusions about hypotheses and theories | Lab Reports |
| 7.10 Apply methods of scientific inquiry and problem solving to contemporary issues | Lab Reports |
Other Course Requirements
- Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 8th Edition. Martini and Bartholomew. (ISBN: 9780135203804)
- Goggles and nitrile gloves
- Dissection equipment
- Dissection specimens
Languages
Course Number NASL-190 Credits 3
Instructor: Marguerite Carrillo
This course is designed for deaf and hard-of-hearing students who have little or no prior skill in American Sign Language. Students will begin to develop receptive and expressive skills needed to converse about familiar topics using a variety of phrases, simple sentences, and questions. Students will learn vocabulary, grammar, and cultural protocols for communicating at a Novice-Low to Novice-Mid ASL level as defined by the American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Languages.
Topics
- 1. Introduction to ASL
- 1.1 Compare and contrast basic parameters for ASL and English
- 1.2 Converse using greetings and introductions
- 1.3 Various types of WH-questions using appropriate sentence structure
- 1.4 Use sentence structure for Yes/No questions
- 1.5 Use cultural behaviors for getting attention and backchanneling
- 2. Time and Activities
- 2.1 ASL basic sentence structure
- 2.2 Express time and activities appropriately in ASL
- 2.3 Fingerspell the months of the year
- 2.4 Use number incorporation for minutes, hours, days, weeks, months, and years
- 2.5 Express past, present, and future tenses in an ASL basic sentence
- 2.6 Use listing on the non-dominant hand for related activities
- 2.7 Topicalization
- 3. Relationships
- 3.1 Exchange basic information about family
- 3.2 List of rank order
- 3.3 Number incorporation for age
- 3.4 Use appropriate shoulder shift to discuss two family members
- 4. Places of Residence
- 4.1 Names of states
- 4.2 Basic pseudo-cleft sentence structures for WHY and WHERE
- 4.3 Establish reference points to specific locations
- 4.4 Sign variation based on geographical differences
- 5. People and Places on Campus
- 5.1 Exchange basic information about people and occupations on campus
- 5.2 Plain and indicating verbs with temporal aspect and continuity
- 5.3 Spatial referencing for locations
- 5.4 Spatial positions for locations within a building
- 5.5 Purpose of using locative and classifiers
- 5.6 Use ordinal numbers
- 5.7 Use signer’s perspective when giving directions
- 5.8 Name signs for places on campus and organizations
- 6. Shopping
- 6.1 Exchange basic information about shopping
- 6.2 Money signs, including using number incorporation
- 6.3 Lexicalized fingerspelling
- 6.4 Possessive pronouns and topicalization when discuss shopping
- 6.5 Listing to discuss purchases, savings and payment methods
- 6.6 Number incorporation with money signs
- 6.7 Lexicalized fingerspelling
- 7. Self-Advocacy Skills
- 7.1 Linguistic Capital in the Deaf Community
- 7.1.1 Sign Language and Learning
- 7.1.2 American Sign Language
- 7.1.3 How Deaf People Think, Learn and Read
- 7.2 Social Capital in the Deaf Community
- 7.2.1 Exploring Deaf Communities in the United States
- 7.1 Linguistic Capital in the Deaf Community
Goals / Learning Outcomes
| Course student learning outcome | Assessment method |
|---|---|
| 1. Develop the ability to perceive language using a visual-gestural modality | |
| 1.1 Demonstrate ability to use body movements and facial expressions | Classroom/online activities; Assignments |
| 1.2 Develop comfort in dealing with the challenges inherent in learning a visual-gestural language | Classroom/online activities; Assignments |
| 1.3 Discriminate the parameters of ASL | Classroom/online activities; Assignments |
| 1.4 Compare and contrast basic English and ASL grammar | Classroom/online activities; Assignments |
| 1.5 Comprehend written information on the nature of language learning and ASL | Written Essay; Written Essay Rubric |
| 2. Develop receptive and expressive communication skills needed to converse about familiar topics using a variety of phrases, simple sentences, and questions | |
| 2.1 Comprehend basic phrases, simple sentences, and questions in ASL at a Novice-Mid level | Classroom/online activities; Assignments; Receptive tests; Final exam |
| 2.2 Express basic phrases, simple sentences, and questions in ASL at a Novice-Mid level | Classroom/online activities; Assignments; Expressive tests; Final exam |
| 2.3 Apply basic appropriate grammar to simple sentences and questions | Classroom/online activities; Assignments; Expressive tests; Final exam |
| 3. Gain self-advocacy skills in linguistic and social aspects in the United States Deaf community | |
| 3.1 Explore one’s own linguistic capital in different languages and ASL | Classroom/online discussion; Reading Assignment; Written Essay; Written Essay Rubric |
| 3.2 Explore their own’s social capital in different communities and in the Deaf community | Classroom/online discussion; Reading Assignment; Written Essay; Written Essay Rubric |
| 4. Engage as an active participant with members of the Deaf community at a Novice-Mid level in familiar situations at school, work, or play | |
| 4.1 Create short dialogues in ASL incorporating basic grammar and cultural protocols | Classroom/online discussions; Evidence of attendance and participation |
| 4.2 Evaluate one’s own ability to communicate with members of the Deaf community | Classroom/online discussions; Evidence of attendance and participation |
| 4.3 Attend and participate in sign-centric events | Classroom/online discussions; Evidence of attendance and participation |
Resources
- Leigh, I. W., Andrews, J. F., & Harris, R. L. (2018). Deaf culture: Exploring deaf communities in the United States. Plural Publishing: San Diego, CA.
- Newell, W., Sanders, C. A., Holcomb, B. R., Holcomb, S. K., Caccamise, F., & Peterson, R. (2010). ASL at work: Student text. San Diego, CA: Dawn Sign Press.
- Kemp, M. (1998). Why is learning American Sign Language a challenge? American Annals of the Deaf, 143(3), 255–259. doi:10.1353/aad.2012.0157
- American Sign Language Dictionary (2020a). https://www.signasl.org/
- American Sign Language Dictionary (2020b). https://www.startasl.com/
- Signing Savvy (2020). https://www.signingsavvy.com/
- American Sign Language University YouTube channel videos. https://www.youtube.com/c/Lifeprint-signs/videos
- ASL THAT YouTube channel videos. https://www.youtube.com/user/chsasl/videos
- Course instructional videos and articles provided in myCourses
Registration
Enrollment
The Project Fast Forward opportunity is open to deaf and hard-of-hearing high school students who want to explore their postsecondary options and experience college-level coursework. Helpful indicators of a possible candidate for the PFF opportunity include, but is not limited to:
- Is the student curious about STEM careers?
- Is the student considering their postsecondary options?
- Does the student want to experience college-level course work?
- Does the student enjoy project-based learning?
- Other academic indicators of a potential student-candidate can include GPA, grades in previous subject area courses, test scores as well as being recommended by high school personnel and meeting course prerequisites.
PFF Award
Description:
The PFF award is intended to support high schools that serve students from traditionally underrepresented communities and/or disadvantaged economic backgrounds. The goal is to see an increase in enrollment into STEM post-secondary programs among deaf and hard-of-hearing students from traditionally underrepresented communities and/or disadvantaged economic backgrounds. The funds can be used for textbooks, software, and hardware directly related to the dual-credit courses offered by RIT/NTID.
Available Funds:
$5,000 per school per year
- Applicants may submit a request for an amount exceeding $5,000 with justification. This is done on a case-by-case basis.
Deadline:
Applications are received and reviewed on a rolling basis. Awards are made as long as funds are available for the calendar year.
Requirements:
Complete the application along with a budget detailing the specific course materials needed and their cost(s). Also include a paragraph outlining the impact the award will have on the students. As a condition for receiving funding, schools receiving this award will commit to teaching dual-credit courses the following academic year with an overall student enrollment of three students or more.
| “ | With the money we received from the PFF award, we were able to purchase all of the equipment and supplies needed to complete the required labs for the RIT/NTID dual-credit biology course as well as replenish normal daily science supplies that were utilized throughout the year. All five of our students who participated in the dual-credit course are pursuing college degrees in the fields of science/math/technology. I think this truly shows how much being exposed to RIT/NTID dual-credit content and curriculum can make a difference in students’ lives. Kathy Craig Science Teacher of the Deaf and Hard of Hearing Hinsdale South High School |
Virtual Project Fast Forward Information Session
Friday, February 10, 2023 at 3:00 PM until 4:00 PM Eastern Daylight Time
Educators who serve deaf and hard-of-hearing high school students are invited to join us for a virtual information session to learn more about the PFF program that provides transformative learning experiences for deaf and hard-of-hearing high school students across the country. PFF provides teachers with the training, resources, and support they need to teach dual-credit courses for FREE at their high schools, and help deaf and hard-of-hearing students earn college credit. An award of up to $5,000 is available to qualified schools per semester. Learn more about this outstanding opportunity!