Mathematical Modeling Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) Degree

Mathematical Modeling
Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) Degree
- RIT /
- Rochester Institute of Technology /
- Academics /
- Mathematical Modeling Ph.D.
Request Info about graduate study
Visit
Apply
School of Mathematics and Statistics
The mathematical modeling Ph.D. enables you to develop mathematical models to investigate, analyze, predict, and solve the behaviors of a range of fields from medicine, engineering, and business to physics and science.
Overview for Mathematical Modeling Ph.D.
Mathematical modeling is the process of developing mathematical descriptions, or models, of real-world systems. These models can be linear or nonlinear, discrete or continuous, deterministic or stochastic, and static or dynamic, and they enable investigating, analyzing, and predicting the behavior of systems in a wide variety of fields. Through extensive study and research, graduates of the mathematical modeling Ph.D. will have the expertise not only to use the tools of mathematical modeling in various application settings, but also to contribute in creative and innovative ways to the solution of complex interdisciplinary problems and to communicate effectively with domain experts in various fields.
Plan of Study
The degree requires at least 60 credit hours of course work and research. The curriculum consists of three required core courses, three required concentration foundation courses, a course in scientific computing and high-performance computing (HPC), three elective courses focused on the student’s chosen research concentration, and a doctoral dissertation. Elective courses are available from within the School of Mathematics and Statistics as well as from other graduate programs at RIT, which can provide application-specific courses of interest for particular research projects. A minimum of 30 credits hours of course work is required. In addition to courses, at least 30 credit hours of research, including the Graduate Research Seminar, and an interdisciplinary internship outside of RIT are required.
Students develop a plan of study in consultation with an application domain advisory committee. This committee consists of the program director, one of the concentration leads, and an expert from an application domain related to the student’s research interest. The committee ensures that all students have a roadmap for completing their degree based on their background and research interests. The plan of study may be revised as needed. Learn more about our mathematical modeling doctoral students and view a selection of mathematical modeling seminars hosted by the department.
Qualifying Examinations
All students must pass two qualifying examinations to determine whether they have sufficient knowledge of modeling principles, mathematics, and computational methods to conduct doctoral research. Students must pass the examinations in order to continue in the Ph.D. program.
The first exam is based on the Numerical Analysis I (MATH-602) and Mathematical Modeling I, II (MATH-622, 722). The second exam is based on the student's concentration foundation courses and additional material deemed appropriate by the committee and consists of a short research project.
Dissertation Research Advisor and Committee
A dissertation research advisor is selected from the program faculty based on the student's research interests, faculty research interest, and discussions with the program director. Once a student has chosen a dissertation advisor, the student, in consultation with the advisor, forms a dissertation committee consisting of at least four members, including the dissertation advisor. The committee includes the dissertation advisor, one other member of the mathematical modeling program faculty, and an external chair appointed by the dean of graduate education. The external chair must be a tenured member of the RIT faculty who is not a current member of the mathematical modeling program faculty. The fourth committee member must not be a member of the RIT faculty and may be a professional affiliated with industry or with another institution; the program director must approve this committee member.
The main duties of the dissertation committee are administering both the candidacy exam and final dissertation defense. In addition, the dissertation committee assists students in planning and conducting their dissertation research and provides guidance during the writing of the dissertation.
Admission to Candidacy
When a student has developed an in-depth understanding of their dissertation research topic, the dissertation committee administers an examination to determine if the student will be admitted to candidacy for the doctoral degree. The purpose of the examination is to ensure that the student has the necessary background knowledge, command of the problem, and intellectual maturity to carry out the specific doctoral-level research project. The examination may include a review of the literature, preliminary research results, and proposed research directions for the completed dissertation. Requirements for the candidacy exam include both a written dissertation proposal and the presentation of an oral defense of the proposal. This examination must be completed at least one year before the student can graduate.
Dissertation Defense and Final Examination
The dissertation defense and final examination may be scheduled after the dissertation has been written and distributed to the dissertation committee and the committee has consented to administer the final examination. Copies of the dissertation must be distributed to all members of the dissertation committee at least four weeks prior to the final examination. The dissertation defense consists of an oral presentation of the dissertation research, which is open to the public. This public presentation must be scheduled and publicly advertised at least four weeks prior to the examination. After the presentation, questions will be fielded from the attending audience and the final examination, which consists of a private questioning of the candidate by the dissertation committee, will ensue. After the questioning, the dissertation committee immediately deliberates and thereafter notifies the candidate and the mathematical modeling graduate director of the result of the examination.
Residency
All students in the program must spend at least two consecutive semesters (summer excluded) as resident full-time students to be eligible to receive the doctoral degree.
Maximum Time Limitations
University policy requires that doctoral programs be completed within seven years of the date of the student passing the qualifying exam. All candidates must maintain continuous enrollment during the research phase of the program. Such enrollment is not limited by the maximum number of research credits that apply to the degree.
National Labs Career Fair
Hosted by RIT’s Office of Career Services and Cooperative Education, the National Labs Career Fair is an annual event that brings representatives to campus from the United States’ federally funded research and development labs. These national labs focus on scientific discovery, clean energy development, national security, technology advancements, and more. Students are invited to attend the career fair to network with lab professionals, learn about opportunities, and interview for co-ops, internships, research positions, and full-time employment.
Students are also interested in: Applied and Computational Mathematics MS
Research
The College of Science consistently receives research grant awards from organizations that include the National Science Foundation, National Institutes of Health, and NASA, which provide you with unique opportunities to conduct cutting-edge research with our faculty members.
Faculty in the School of Mathematics and Statistics conducts research on a broad variety of topics including:
- applied inverse problems and optimization
- applied statistics and data analytics
- biomedical mathematics
- discrete mathematics
- dynamical systems and fluid dynamics
- geometry, relativity, and gravitation
- mathematics of earth and environment systems
- multi-messenger and multi-wavelength astrophysics
Learn more by exploring the school’s mathematics research areas.
Featured Profiles
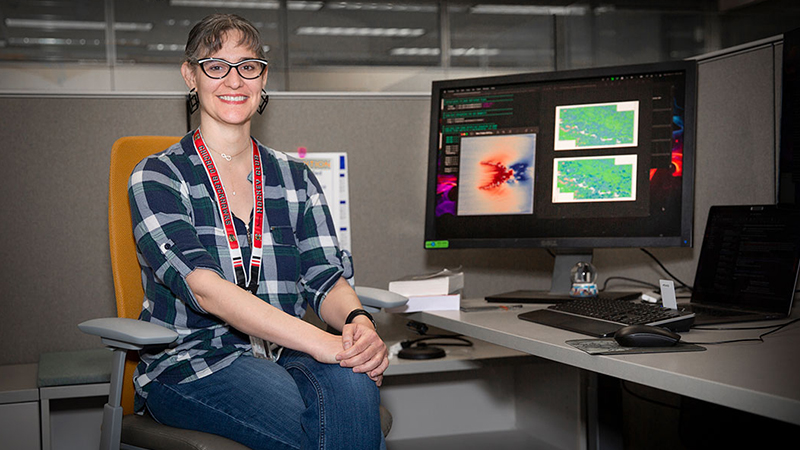
Ph.D. student explores fire through visual art and math modeling
Mathematical Modeling Ph.D. student, Jenna Sjunneson McDanold, explores fire through visual art and mathematical modeling.
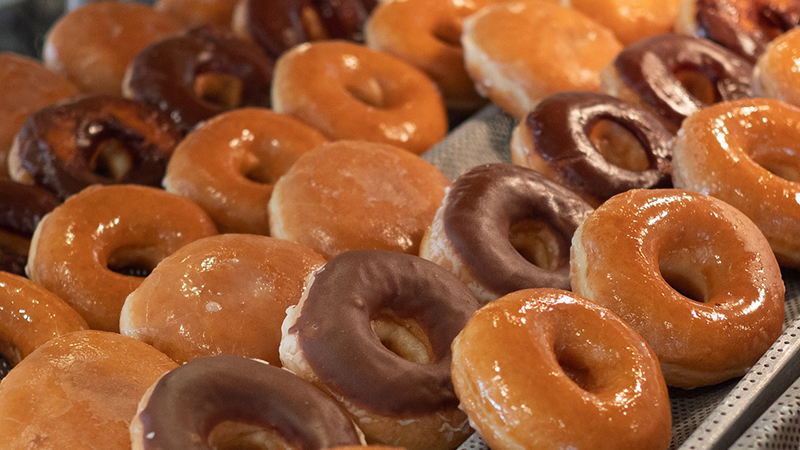
Mathematical Modeling, Curtain Coating, and Glazed Donuts
Bridget Torsey (Mathematical Modeling)
In her research, Bridget Torsey, a Math Modeling Ph.D. student, developed a mathematical model that can optimize curtain coating processes used to cover donuts with glaze so they taste great.
Your Partners in Success: Meet Our Faculty, Dr. Wong
Dr. Tony Wong
Mathematics is a powerful tool for answering questions. From mitigating climate risks to splitting the dinner bill, Professor Wong shows students that math is more than just a prerequisite.
Latest News
-
May 6, 2024
![Nastaran Nagshineh is shown with other faculty in a small room where she defended her thesis.]()
RIT graduate pursues Ph.D. across time zones
Nastaran Nagshineh, a Ph.D. candidate at RIT, successfully bridged the Rochester and Dubai campuses, paving the way for future international students. Nagshineh is one of 67 Ph.D. students who defended their thesis this academic year and who will earn their doctorate.
-
February 22, 2024
![an arial photo of the amazon shows a large amount of deforestation]()
RIT researchers highlight the changing connectivity of the Amazon rainforest to global climate
The Amazon rainforest is a unique region where climatologists have studied the effects of warming and deforestation for decades. With the global climate crisis becoming more evident, a new study is linking the Amazon to climate change around the rest of the world.
-
May 8, 2023
![close up of shampoo, showing large and small purple, yellow and orange bubbles.]()
Squishing the barriers of physics
Four RIT faculty members are opening up soft matter physics, sometimes known as “squishy physics,” to a new generation of diverse scholars. Moumita Das, Poornima Padmanabhan, Shima Parsa, and Lishibanya Mohapatra are helping RIT make its mark in the field.
Curriculum Update in Process for 2024-2025 for Mathematical Modeling Ph.D.
Current Students: See Curriculum Requirements
Mathematical Modeling, Ph.D. degree, typical course sequence
| Course | Sem. Cr. Hrs. | |
|---|---|---|
| First Year | ||
| MATH-602 | Numerical Analysis I This course covers numerical techniques for the solution of nonlinear equations, interpolation, differentiation, integration, and matrix algebra. (Prerequisites: MATH-411 or equivalent course and graduate standing.) Lecture 3 (Fall). |
3 |
| MATH-606 | Graduate Seminar I The course prepares students to engage in activities necessary for independent mathematical research and introduces students to a broad range of active interdisciplinary programs related to applied mathematics. (This course is restricted to students in the ACMTH-MS or MATHML-PHD programs.) Lecture 2 (Fall). |
1 |
| MATH-607 | Graduate Seminar II This course is a continuation of Graduate Seminar I. It prepares students to engage in activities necessary for independent mathematical research and introduces them to a broad range of active interdisciplinary programs related to applied mathematics. (Prerequisite: MATH-606 or equivalent course or students in the ACMTH-MS or MATHML-PHD programs.) Lecture 2 (Spring). |
1 |
| MATH-622 | Mathematical Modeling I This course will introduce graduate students to the logical methodology of mathematical modeling. They will learn how to use an application field problem as a standard for defining equations that can be used to solve that problem, how to establish a nested hierarchy of models for an application field problem in order to clarify the problem’s context and facilitate its solution. Students will also learn how mathematical theory, closed-form solutions for special cases, and computational methods should be integrated into the modeling process in order to provide insight into application fields and solutions to particular problems. Students will study principles of model verification and validation, parameter identification and parameter sensitivity and their roles in mathematical modeling. In addition, students will be introduced to particular mathematical models of various types: stochastic models, PDE models, dynamical system models, graph-theoretic models, algebraic models, and perhaps other types of models. They will use these models to exemplify the broad principles and methods that they will learn in this course, and they will use these models to build up a stock of models that they can call upon as examples of good modeling practice. (This course is restricted to students in the ACMTH-MS or MATHML-PHD programs.) Lecture 3 (Fall). |
3 |
| MATH-722 | Mathematical Modeling II This course will continue to expose students to the logical methodology of mathematical modeling. It will also provide them with numerous examples of mathematical models from various fields. (Prerequisite: MATH-622 or equivalent course.) Lecture 3 (Spring). |
3 |
MATH Concentration Courses |
6 | |
MATH Elective |
3 | |
| Second Year | ||
| MATH-751 | High-performance Computing For Mathematical Modeling Students in this course will study high-performance computing as a tool for solving problems related to mathematical modeling. Two primary objectives will be to gain experience in understanding the advantages and limitations of different hardware and software options for a diverse array of modeling approaches and to develop a library of example codes. The course will include extensive hands-on computational (programming) assignments. Students will be expected to have a prior understanding of basic techniques for solving mathematical problems numerically. (Prerequisite: MATH-602 or equivalent course.) Lecture 3 (Spring). |
3 |
| MATH-790 | Research & Thesis Masters-level research by the candidate on an appropriate topic as arranged between the candidate and the research advisor. (This course is restricted to students in the ACMTH-MS or MATHML-PHD programs.) Thesis (Fall, Spring, Summer). |
7 |
MATH Concentration Course |
3 | |
MATH Electives |
6 | |
| Third Year | ||
| MATH-790 | Research & Thesis Masters-level research by the candidate on an appropriate topic as arranged between the candidate and the research advisor. (This course is restricted to students in the ACMTH-MS or MATHML-PHD programs.) Thesis (Fall, Spring, Summer). |
9 |
| Fourth Year | ||
| MATH-790 | Research & Thesis Masters-level research by the candidate on an appropriate topic as arranged between the candidate and the research advisor. (This course is restricted to students in the ACMTH-MS or MATHML-PHD programs.) Thesis (Fall, Spring, Summer). |
6 |
| Fifth Year | ||
| MATH-790 | Research & Thesis Masters-level research by the candidate on an appropriate topic as arranged between the candidate and the research advisor. (This course is restricted to students in the ACMTH-MS or MATHML-PHD programs.) Thesis (Fall, Spring, Summer). |
6 |
| Total Semester Credit Hours | 60 |
|
Concentrations
Applied Inverse Problems
| Course | Sem. Cr. Hrs. | |
|---|---|---|
| MATH-625 | Applied Inverse Problems Most models in applied and social sciences are formulated using the broad spectrum of linear and nonlinear partial differential equations involving parameters characterizing specific physical characteristics of the underlying model. Inverse problems seek to determine such parameters from the measured data and have many applications in medicine, economics, and engineering. This course will provide a thorough introduction to inverse problems and will equip students with skills for solving them. The topics of the course include existence results, discretization, optimization formulation, and computational methods. (Prerequisites: MATH-431 or equivalent course or graduate student standing.) Lecture 3 (Fall). |
3 |
| MATH-633 | Measure Theory of Elements and Functional Analysis This course will provide a general introduction to Lebesgue measure as applied to the real numbers, real-valued functions of a real variable, and the Lebesgue integral of such functions. It also covers topics in functional analysis relevant to application of measure theory to real-world problems. Students will be expected to read and understand proofs, and to demonstrate their understanding of topics by writing their own proofs of various facts. (Prerequisites: Graduate student standing in COS, GCCIS or KGCOE or B+ or better in MATH 432 or equivalent course.) Lecture 3 (Fall). |
3 |
| MATH-741 | Partial Differential Equations I This course uses methods of applied mathematics in the solution of problems in physics and engineering. Models such as heat flow and vibrating strings will be formulated from physical principles. Characteristics methods, maximum principles, Green's functions, D'Alembert formulas, weak solutions and distributions will be studied. (Prerequisites: MATH-231 or equivalent course or graduate student standing in ACMTH-MS or MATHML-PHD programs.) Lecture 3 (Spring). |
3 |
Biomedical Mathematics
| Course | Sem. Cr. Hrs. | |
|---|---|---|
| MATH-631 | Dynamical Systems This course is a study of dynamical systems theory. Basic definitions of dynamical systems are followed by a study of maps and time series. Stability theory of solutions of differential equations is studied. Asymptotic behavior of solutions is investigated through limit sets, attractors, Poincaré–Bendixson theory, and index theory. The notion of local bifurcation is introduced and investigated. Chaotic systems are studied. (Prerequisites: (MATH-231 and (MATH 241 or MATH-241H)) or equivalent courses or graduate standing in ACMTH-MS or MATHML-PHD programs.) Lecture 3 (Fall). |
3 |
| MATH-702 | Numerical Analysis II The course covers the solutions of linear systems by direct and iterative methods, numerical methods for computing eigenvalues, theoretical and numerical methods for unconstrained and constrained optimization, and Monte-Carlo simulation. (Prerequisite: MATH-602 or equivalent course and graduate standing.) Lecture 3 (Spring). |
3 |
| MATH-761 | Mathematical Biology This course introduces areas of biological sciences in which mathematics can be used to capture essential interactions within a system. Different modeling approaches to various biological and physiological phenomena are developed (e.g., population and cell growth, spread of disease, epidemiology, biological fluid dynamics, nutrient transport, biochemical reactions, tumor growth, genetics). The emphasis is on the use of mathematics to unify related concepts. (Graduate Science) Lecture 3 (Fall). |
3 |
Discrete Mathematics
| Course | Sem. Cr. Hrs. | |
|---|---|---|
| CSCI-665 | Foundations of Algorithms This course provides an introduction to the design and analysis of algorithms. It covers a variety of classical algorithms and their complexity and will equip students with the intellectual tools to design, analyze, implement, and evaluate their own algorithms. Note: students who take CSCI-261 or CSCI-264 may not take CSCI-665 for credit. (Prerequisites: (CSCI-603 and CSCI-605 and CSCI-661 with grades of B or better) or ((CSCI-243 or SWEN-262) and (CSCI-262 or CSCI-263)) or equivalent courses. This course is restricted to COMPSCI-MS, COMPSCI-BS/MS, or COMPIS-PHD students.) Lec/Lab 3 (Fall, Spring). |
3 |
| MATH-645 | Graph Theory This course introduces the fundamental concepts of graph theory. Topics to be studied include graph isomorphism, trees, network flows, connectivity in graphs, matchings, graph colorings, and planar graphs. Applications such as traffic routing and scheduling problems will be considered. (This course is restricted to students with graduate standing in the College of Science or Graduate Computing and Information Sciences.) Lecture 3 (Fall). |
3 |
| MATH-646 | Combinatorics This course introduces the fundamental concepts of combinatorics. Topics to be studied include counting techniques, binomial coefficients, generating functions, partitions, the inclusion-exclusion principle and partition theory. (This course is restricted to students in the ACMTH-MS or MATHML-PHD programs.) Lecture 3 (Spring). |
3 |
Dynamical Systems and Fluid Dynamics
| Course | Sem. Cr. Hrs. | |
|---|---|---|
| MATH-631 | Dynamical Systems This course is a study of dynamical systems theory. Basic definitions of dynamical systems are followed by a study of maps and time series. Stability theory of solutions of differential equations is studied. Asymptotic behavior of solutions is investigated through limit sets, attractors, Poincaré–Bendixson theory, and index theory. The notion of local bifurcation is introduced and investigated. Chaotic systems are studied. (Prerequisites: (MATH-231 and (MATH 241 or MATH-241H)) or equivalent courses or graduate standing in ACMTH-MS or MATHML-PHD programs.) Lecture 3 (Fall). |
3 |
| MATH-741 | Partial Differential Equations I This course uses methods of applied mathematics in the solution of problems in physics and engineering. Models such as heat flow and vibrating strings will be formulated from physical principles. Characteristics methods, maximum principles, Green's functions, D'Alembert formulas, weak solutions and distributions will be studied. (Prerequisites: MATH-231 or equivalent course or graduate student standing in ACMTH-MS or MATHML-PHD programs.) Lecture 3 (Spring). |
3 |
| MATH-831 | Mathematical Fluid Dynamics The study of the dynamics of fluids is a central theme of modern applied mathematics. It is used to model a vast range of physical phenomena and plays a vital role in science and engineering. This course provides an introduction to the basic ideas of fluid dynamics, with an emphasis on rigorous treatment of fundamentals and the mathematical developments and issues. The course focuses on the background and motivation for recent mathematical and numerical work on the Euler and Navier-Stokes equations, and presents a mathematically intensive investigation of various models equations of fluid dynamics. (Prerequisite: MATH-741 or equivalent course.) Lecture 3 (Fall, Spring, Summer). |
3 |
Geometry, Relativity and Gravitation
| Course | Sem. Cr. Hrs. | |
|---|---|---|
| ASTP-660 | Introduction to Relativity and Gravitation This course is the first in a two-course sequence that introduces Einstein’s theory of General Relativity as a tool in modern astrophysics. The course will cover various aspects of both Special and General Relativity, with applications to situations in which strong gravitational fields play a critical role, such as black holes and gravitational radiation. Topics include differential geometry, curved spacetime, gravitational waves, and the Schwarzschild black hole. The target audience is graduate students in the astrophysics, physics, and mathematical modeling (geometry and gravitation) programs. (This course is restricted to students in the ASTP-MS, ASTP-PHD, MATHML-PHD and PHYS-MS programs.) Lecture 3 (Fall). |
3 |
| ASTP-861 | Advanced Relativity and Gravitation This course is the second in a two-course sequence that introduces Einstein’s theory of General Relativity as a tool in modern astrophysics. The course will cover various aspects of General Relativity, with applications to situations in which strong gravitational fields play a critical role, such as black holes and gravitational radiation. Topics include advanced differential geometry, generic black holes, energy production in black-hole physics, black-hole dynamics, neutron stars, and methods for solving the Einstein equations. The target audience is graduate students in the astrophysics, physics, and mathematical modeling (geometry and gravitation) programs. (Prerequisite: ASTP-660 or equivalent course.) Lecture 3 (Spring). |
3 |
| MATH-702 | Numerical Analysis II The course covers the solutions of linear systems by direct and iterative methods, numerical methods for computing eigenvalues, theoretical and numerical methods for unconstrained and constrained optimization, and Monte-Carlo simulation. (Prerequisite: MATH-602 or equivalent course and graduate standing.) Lecture 3 (Spring). |
3 |
Admissions and Financial Aid
This program is available on-campus only.
| Offered | Admit Term(s) | Application Deadline | STEM Designated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full‑time | Fall. Closed for new applications for Fall 2024. | January 15 priority deadline, rolling thereafter | Yes |
Full-time study is 9+ semester credit hours. International students requiring a visa to study at the RIT Rochester campus must study full‑time.
Application Details
To be considered for admission to the Mathematical Modeling Ph.D. program, candidates must fulfill the following requirements:
- Complete an online graduate application.
- Submit copies of official transcript(s) (in English) of all previously completed undergraduate and graduate course work, including any transfer credit earned.
- Hold a baccalaureate degree (or US equivalent) from an accredited university or college.
- A recommended minimum cumulative GPA of 3.0 (or equivalent).
- Submit a current resume or curriculum vitae.
- Submit a statement of purpose for research which will allow the Admissions Committee to learn the most about you as a prospective researcher.
- Submit two letters of recommendation.
- Entrance exam requirements: None
- Writing samples are optional.
- Submit English language test scores (TOEFL, IELTS, PTE Academic), if required. Details are below.
English Language Test Scores
International applicants whose native language is not English must submit one of the following official English language test scores. Some international applicants may be considered for an English test requirement waiver.
| TOEFL | IELTS | PTE Academic |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 7.0 | 70 |
International students below the minimum requirement may be considered for conditional admission. Each program requires balanced sub-scores when determining an applicant’s need for additional English language courses.
How to Apply Start or Manage Your Application
Cost and Financial Aid
An RIT graduate degree is an investment with lifelong returns. Ph.D. students typically receive full tuition and an RIT Graduate Assistantship that will consist of a research assistantship (stipend) or a teaching assistantship (salary).
Additional Information
Foundation Courses
Mathematical modeling encompasses a wide variety of scientific disciplines, and candidates from diverse backgrounds are encouraged to apply. If applicants have not taken the expected foundational course work, the program director may require the student to successfully complete foundational courses prior to matriculating into the Ph.D. program. Typical foundation course work includes calculus through multivariable and vector calculus, differential equations, linear algebra, probability and statistics, one course in computer programming, and at least one course in real analysis, numerical analysis, or upper-level discrete mathematics.